Highlights
- Wounds and injuries may damage the skin or break the tissue causing infections.
- A new compound made of bamboo cellulose and silver nanoparticles were found to treat skin injuries.
- The new wound-dressing material is capable of healing wounds completely, and allows regeneration of new skin cells.
Sudesh Kumar, a scientist at Centre of Innovative and Applied Bioprocessing in Punjab, said, “An effective wound healing or a dressing material is needed that can cater moist environment to wound, prevent microbial infection and can be readily removed from the wound site without causing much pain.”
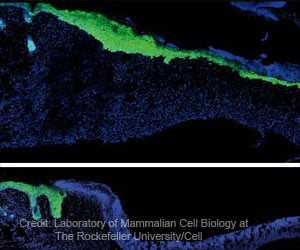
The research team from Delhi were found to synthesize nanobiocomposites, by inserting silver nanoparticles into the cellulose nanocrystals obtained from two species of bamboo leaves.
Selection of Bamboo Plant
- Capable of growing faster
- It has a longest internode segment that allows to isolate cellulose nanocrystals.
How Does it Work?
An overnight incubation of nanocomposites material with infectious bacteria was found to provide strong antibacterial activity.
They induce the growth of collagen materials and stops the proliferation of immune cells that trigger inflammation, and prolong healing.
Kumar, said, “Among biomedical applications, wound repair has been a realm of extensive research over a past few decades. Plants are the natural largest source of cellulose, but are largely unexplored in such biomedical applications.”
Benefits of the New Wound-Healing Material
- Complete healing of skin wounds
- Keeps the wound site moist
- Stimulates certain enzymes and allows regeneration of skin cells
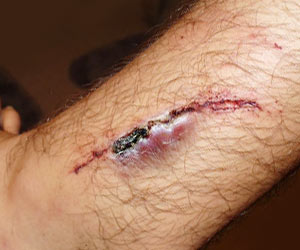
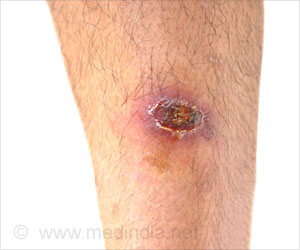
Wound or Injuries
Wound or injury may break the tissue or damage the skin causing infections. There are a number of wound-healing materials made of biopolymers to treat wound and injuries.
Drawbacks with Current Wound-Dressing Materials
- Foul Smell
- Low Porosity
- Poor-Healing Capacity
- Toxic to Biological Cells
- Wounds and Injuries - (https://medlineplus.gov/woundsandinjuries.html)
Source-Medindia