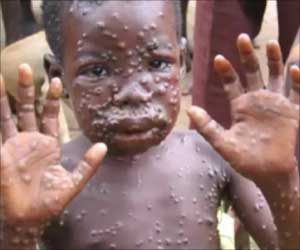
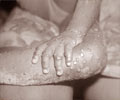
- Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, which is a viral zoonotic disease meaning that it is usually transmitted from animals to humans and also through close contact with an infected person.
- The clinical profile of monkeypox resembles that of smallpox, a related viral infection that was eradicated globally in 1980.
- Symptoms include fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes and a skin rash or lesions.
- The prognosis depends on various factors like previous vaccination status, initial health condition, co-morbidities and treatment taken
Monkeypox
Go to source). As monkeypox and smallpox viruses are genetically identical, the antiviral drugs and vaccines used against smallpox may prevent and treat monkeypox infections (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Treatment
Go to source).
Read More..
Vaccines Against Monkeypox
-
JYNNEOS or Imvamune or Imvanex
: This vaccine has been licensed in the United States to prevent monkeypox and smallpox. As the monkeypox virus is closely related to the smallpox virus, the smallpox vaccine can also protect people from getting monkeypox. It is administered as a live virus that is non-replicating, as two subcutaneous injections four weeks apart. People with this vaccine are not considered vaccinated until two weeks after receiving the second dose of the vaccine (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Interim Clinical Guidance for the Treatment of Monkeypox
Go to source). ACAM2000 vaccine :
This vaccine can be used in individuals exposed to monkeypox if used under an expanded access investigational new drug protocol. It contains a live virus. It is approved for vaccination in individuals aged above 18 years who are at high risk for smallpox infection. After vaccination, a lesion will develop at the site of the vaccination. The virus grows at the site and can spread to other body parts or close contacts.Vaccinia Immune Globulin (VIG):
Health care providers may consider VIG use in severe monkeypox cases. VIG can be considered for prophylactic purposes in patients with severe immunodeficiency, for which smallpox vaccination is contraindicated after exposure to the monkeypox virus.
Receiving Vaccine After Exposure to Monkeypox
Persons exposed to the monkeypox virus and who have not received the smallpox vaccine within the last three years should consider getting vaccinated.The sooner an exposed individual gets the vaccine, the better. CDC recommends providing vaccine within four days from the date of exposure. Given during 4 to 14 days, vaccination may decrease the symptoms of the disease but may not prevent the disease.
Available Medical Countermeasures for Monkeypox
Currently, there is no approved specific treatment for monkeypox. But antivirals developed for smallpox may provide some benefits (3✔ ✔Trusted SourceInterim Clinical Guidance for the Treatment of Monkeypox
Go to source).
The following counter measures are currently available from the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS):
-
Tecovirimat or TPOXX, ST-246
: It is an antiviral drug approved by the U.S. FDA for treating smallpox in children and adults. This medication is available as a pill or an injection (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Highlights of Prescribing Information
Go to source). Cidofovir
: It is an antiviral drug that is used for treating Cytomegalovirus(CMV) retinitis (inflammation of the inner layer of the eye) in patients with AIDS/HIV.Brincidofovir
: It is an antiviral drug that is approved by the U.S. FDA for treating human smallpox in adults and children, including neonates.
References:
- Monkeypox - (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/monkeypox)
- Treatment - (https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/treatment.html)
- Interim Clinical Guidance for the Treatment of Monkeypox - (https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/clinicians/treatment.html#:~:text=At%20this%20time%2C%20there%20are,to%20control%20a%20monkeypox%20outbreak)
- Highlights of Prescribing Information - (https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/208627s000lbl.pdf)
Source-Medindia