- Residual renal function should be preserved even in hemodialysis patients
- Residual renal function can be predicted using trace protein (βTP) and β2-microglobulin (β2M)
- βTP and β2M concentrations were found to reasonably predict concentrations of residual urea clearance of 2 ml/min/1.73 m2 or more.
Significance of Residual Kidney Function
Hemodialysis is not qualitatively equivalent to residual renal function and, therefore, the residual renal function should be preserved.
- Clearance of small solutes
- Helps in the maintaining the fluid balance
- Maintaining phosphorous control
- Improving anemia
- Elimination of uremic toxins of middle molecular weight
- Cardiac hypertrophy
- Valvular calcification
- Anemia
- Malnutrition
- Inflammation
Residual renal function is very significant among patients on dialysis. The Kidney Diseases Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) guidelines indicate that hemodialysis can be reduced among patients with 2 ml/min/1.73 m2 or more of Residual Urea Clearance (KRU). This requires routine monitoring of the residual renal function.
Drawbacks in the Current Method of Measuring Residual Renal Function
The current methods for assessing residual renal function have the following limitationsA. The method involves collecting interdialytic urine which is relatively complicated
B. Urea and creatinine clearance are measured which are also dependent on the muscle mass, gender and diet of the individual.
This makes prediction of residual renal function difficult. The latest study by Wong et al. and colleagues in the paper titled “Predicting residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients using serum β-trace protein and β2-microglobulin” in the journal Kidney International (May 2016) identifies a better marker.
βTP is also called lipocali- type prostaglandin D synthase. This 23 kDa glycoprotein is excreted exclusively by the kidneys but is present in the brain, heart, retina, testis and kidney. The residual urine output has been correlated with βTP concentrations but the study by Wang et al. is the first to explore its relevance in identifying residual kidney function among hemodialysis patients.
Properties of β2M:
Equations to Predict GFR and KRU Using βTP and β2M
231 patients on hemodialysis were included in the study. 191 patients were assessed to model the equation for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and residual urea clearance (KRU) while the rest 40 patients were used to validate the earlier findings.The trace proteins were used to determine the linear regression model for GFR and KRU using only
- βTP
- β2M
- Both β2M and βTP
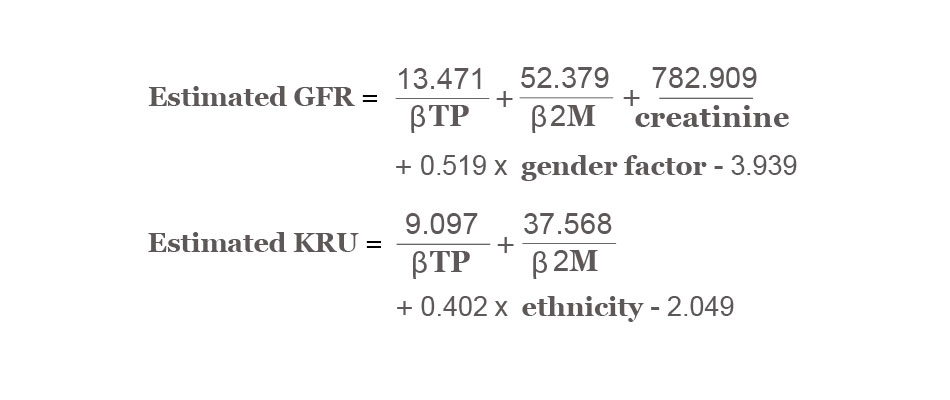
Source: Jonathan Wong, Sivakumar Sridharan Jocelyn Berdeprado, Enric Vilar1, Adie Viljoen, David Wellsted, Ken Farrington; “Predicting residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients using serum β-trace protein and β2-microglobulin”; Kidney International, May 2016.
Validation of the Equations:
The values of GFR and KRU obtained using the equation were validated by assessed using the validation study participants. It was found that estimation and validation values from the respective study subjects correlated significantly.
The equations were used to study the value of KRU and to follow KDOQI guidelines in altering hemodialysis. The value of KRU estimated using the equations in the study correlated with measured KRU values.
Though the study sample used for validation was small, the results of the study show promise for a better method of estimation of KRU. This would limit the need for interdialytic urine collection and provide a better monitoring system.
References:
- Jonathan Wong, Sivakumar Sridharan Jocelyn Berdeprado, Enric Vilar1, Adie Viljoen, David Wellsted, Ken Farrington; “Predicting residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients using serum β-trace protein and β2-microglobulin”; Kidney International, May 2016
- A.Y.-M. Wang, K.-N. Lai, “The importance of residual renal function in dialysis patients”, Kidney International, May 2006.
- Measurement of residual renal function in HD
http://ndt.oxfordjournals.org/content/17/suppl_7/11.abstract