Highlights:
- New stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (exosomes) found to improve healing and be effective in reducing stroke-induced damage to brain tissue
- Stroke (impaired blood flow) induced brain damage is estimated to be the second leading cause of death globally and the third leading cause of disability.
Initial Testing of EV Therapy In Rodent Models Of Stroke
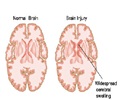
The study team led by UGA professor Steven Stice and Nasrul Hoda of Augusta University created a treatment called AB126 composed of extracellular vesicles derived from human nerve stem cells. Following the administration of AB126 in preclinical age-matched rodent stroke models, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans were done to measure the degree of brain damage. The findings in treated mice were as follows- Nearly 35 percent decrease in the size of brain injury
- 50 percent decrease in brain tissue loss – higher than previous studies that tested EV therapy for stroke
"This is truly exciting evidence because exosomes provide a stealth-like characteristic, invisible even to the body's own defenses," said Stice, Georgia Research Alliance Eminent Scholar, and D.W. Brooks Distinguished Professor in the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences. "When packaged with therapeutics, these treatments can actually change cell progression and improve functional recovery."
Adds Stice, "Until now, we had very little evidence specific to neural exosome treatment and the ability to improve motor function," said Stice. "Just days after stroke, we saw better mobility, improved balance, and measurable behavioral benefits in treated animal models."
About Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are cell-derived vesicles found in almost all eukaryotic fluids, including blood, urine, and culture medium of cell cultures. They can potentially be used as biomarkers as well as in the treatment of disease.Due to their minute size (less than 100 nm) and unique properties exosomes offer several distinct advantages as drug delivery options, overcoming the limitations of current stem cell-based therapies and crossing barriers that cells cannot.
Limitations of Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cell-based treatments are highly popular in several diseases including stroke. However, stem cell therapy has certain limitations such as- Limited supply of stem cells in aged patients
- Decrease in tropism of stem cells towards brain over time
- Limited nerve regenerative potential especially in elderly patients and those with chronic illness
- Adverse effects such as tumor formation, immune rejection, stem cells trapping in lungs and blood vessels
Future
Plans Based on Current Study
- ArunA plans to manufacture AB126 exosomes at a scale to satisfy early clinical demand
- Plans to employ and expand this platform for other preclinical studies such as epilepsy, spinal cord, and traumatic brain injury later this year
- Development of technology to create low cost, high-quality tools to revolutionize treatment of cancer, stroke, heart disease and other diseases.
References:
- Adult Stem Cell Therapy for Stroke: Challenges and Progress - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5066440/)
- Exosome (vesicle) - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exosome_(vesicle)#Therapeutics_and_carriers_of_drugs)
Source-Medindia