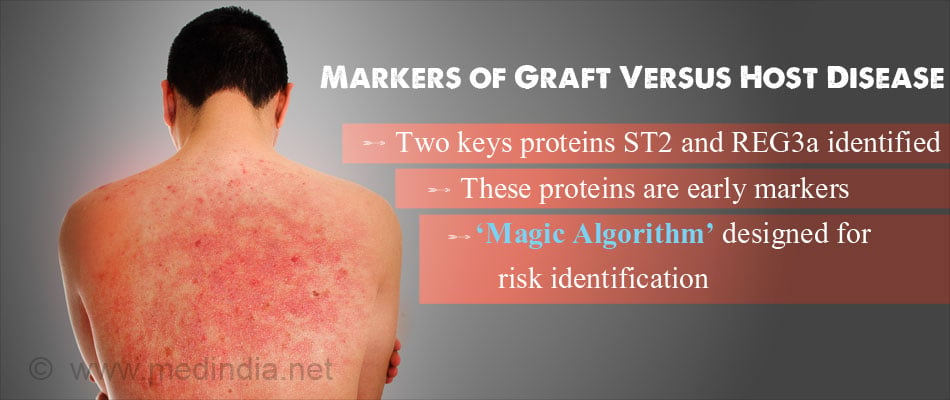
- Scientists from Mount Sinai Health system have identified 2 key proteins ST2 and REG3a which are found one week after bone marrow transplant
- This will aid in early identification of graft versus host disease among blood cancer patients who receive a bone marrow transplant
- ‘MAGIC algorithm’ designed by the scientists can be used for determining the risk of disease
The findings of the study were
- ST2 and REG3a are two proteins found in the blood of the bone marrow transplant patients a week after the transplant. These proteins could be used to predict whether the dangerous graft-versus-host disease would occur.
- This aided in prediction long before symptoms were developed.
MAGIC Algorithm
Professor of Pediatrics, Dr. James L.M. Ferrara from The Tisch Cancer Institute said that the MAGIC algorithm provides doctors with a map of how the transplant patients would react to transplantation, saving many lives. This can be used for early identification and intervention which could save many lives.Saving Lives
The doctors at Mount Sinai are structuring clinical trials to identify if immunotherapeutic drugs would aid patients in lowering the severity of the disease once the proteins are identified in the blood stream. The scientists hope that drug interventions would lower the intensity of the graft rejection disease and result in fewer deaths.
Co-director of MAGIC, Dr. John Levine who is also a Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine at the Tisch Cancer Institute (Mount Sinai) said that the test that has been developed will aid in making bone marrow transplant safer and will allow personalization of medications in order to prevent graft versus host disease. The scientists are eagerly waiting for the success of the clinical trials that are being planned in order to begin using the immune therapy drugs as a standard form of care for patients who undergo a bone marrow transplant.
Graft Versus Host Disease (GvHD)
When a blood cancer patient needs to undergo a bone marrow transplant, the tissue of the donor is analyzed and checked before transplant to ensure that it is a close match with the recipient. The risk of rejection is lowered when the donor tissue and cells match with that of the recipient.Risk of Graft Versus Host Disease
- When the donor and the recipient are related, the risk is between 30-40%
- When the donor and the recipient are not related, the risk is between 60-80%
The chronic form of graft versus host disease is characterized by symptoms that begin after 3 months from the time of transplant and last for the rest of the lifetime of the patient. The symptoms include dry mouth, dry eyes, changes in vision, sensitivity to food rich in spices, chronic pain in the joint and stiffness, breathlessness due to damage to the lung, muscle weakness, fatigue, discoloration, skin tightening or thickening. This could also be associated with weight loss and vaginal dryness.
Currently, imaging and laboratory tests are used to monitor symptoms associated with this disease condition. To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy of the skin as well as the mucous membrane is analyzed.
The prognosis of a patient suffering from graft versus host disease depends on how severe the disease is. The outlook is better for patients who have received bone marrow transplant from closely matched donors. In severe forms of the disease, the lungs, digestive tract, liver or other parts of the body may be affected. Some people with the disease may be treated successfully but it could be fatal in many others.
The current study which has identified that the presence of two proteins as early markers of the disease could aid in faster detection and better care. The MAGIC algorithm designed by the scientists will aid doctors in identifying the best method of treatment for the patient which could revolutionize bone marrow transplant post-operative care.
References:
- Graft-versus-host disease - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001309.htm)