‘SERPINB gene cluster on chromosome 18 was identified as a specific genetic risk locus for food allergies.’
Tweet it Now
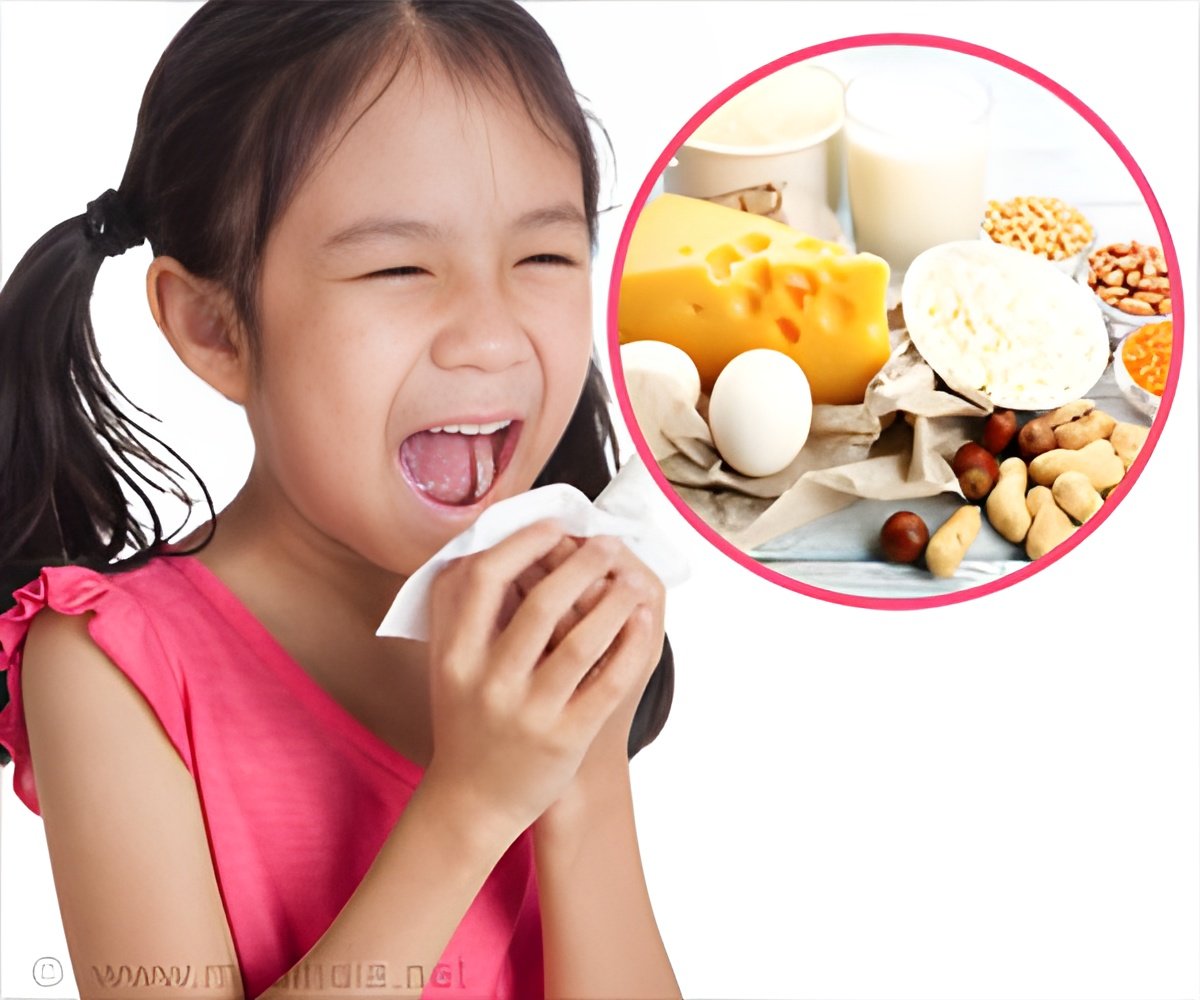
In Germany, chicken eggs, cow’s milk, and peanuts are the most common causes of allergic food reactions in children. Unlike allergies to cow’s milk and chicken eggs, which often disappear after a few years, children generally do not outgrow allergies to peanuts. Peanut allergy sufferers must follow a strict diet for their entire lives and carry emergency medication with them at all times. The causes of food allergies involve a complex interplay of genetics and environment. "Studies of twins suggest that about 80 percent of the risk for food allergies is heritable, but little is known so far about these genetic risk factors," says Prof. Young-Ae Lee, a researcher at the MDC and head of the Charité’s outpatient pediatric allergy clinic.
World’s largest study into the genetic causes of food allergies
A genome-wide association study examined some 1,500 children in Germany and the United States who suffer from food allergies. The research looked at more than five million genetic variations, called single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips"), in each participant in the study and compared the frequency of these SNPs with that of the control subjects. The study, which was published in Nature Communications, involved researchers from Berlin, Frankfurt, Greifswald, Hanover, Wangen, and Chicago. It is remarkable not only for its size but also for its reliable diagnostic methodology.
Unlike other studies, the researchers used an oral food challenge test to confirm the allergy diagnosis. This is a complex procedure in which patients ingest small amounts of the suspected allergen in the hospital under emergency conditions to determine if they respond allergically to it. "We know from clinical practice that as many as 80 percent of presumed food allergies are not actually allergies. These food sensitivities are frequently due to food intolerance rather than an allergic response," says Prof. Lee.
Advertisement
New risk locus associated with all children’s food allergies
Advertisement
The study provides a basis for the development of better diagnostic tests for food allergies and for further investigation into their causative mechanisms and possible treatment strategies. Parents should not make decisions about avoiding specific foods on their own, but should instead seek out a specialist if their child appears to have a food allergy.
Source-Eurekalert