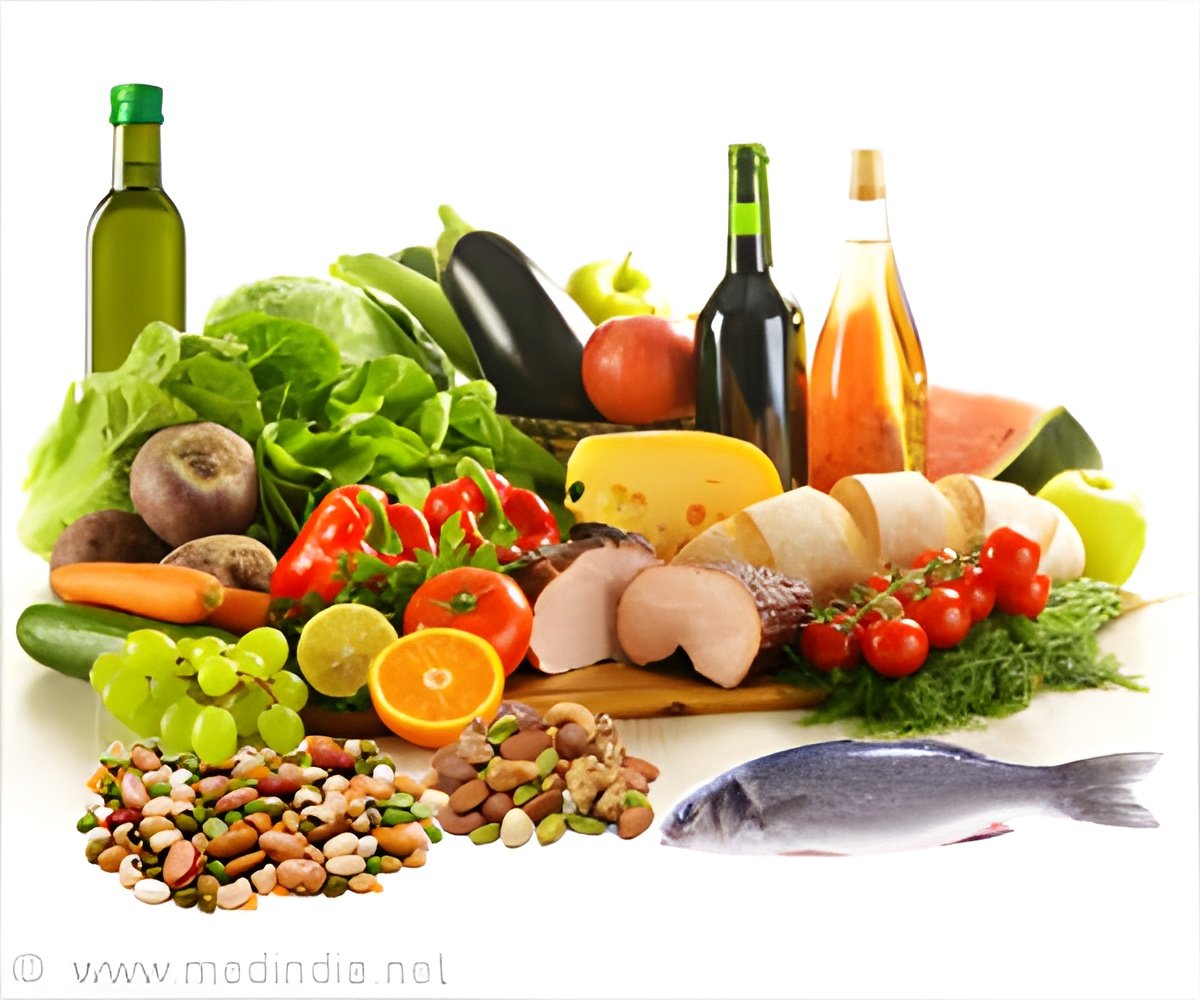
‘People at risk of heart attack can follow a Mediterranean diet as it decreases the chances of such cardiovascular events.’
Tweet it Now
The study was conducted among 15,482 people who were asked to fill a questionnaire. There were given a “Mediterranean diet score” (MDS) for healthy foods consumption and a “Western Diet Score,” for consuming unhealthy foods based on their answers.Healthy foods included fruits, vegetables, while unhealthy foods were deep fried and sugary foods. They found that every one unit raise in MDS was associated with a 7% reduction in the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events in patients with existing heart disease.
“After adjusting for other factors that might affect the results, we found that every one unit increase in the Mediterranean Diet Score was associated with a seven percent reduction in the risk of heart attacks, strokes or death from cardiovascular or other causes in patients with existing heart disease,” says lead researcher Ralph Stewart from the Auckland City Hospital, University of Auckland, New Zealand.
Source-Medindia