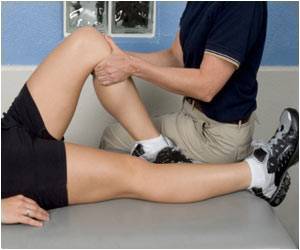
‘Rupture of the Achilles tendon is a serious and increasingly common injury with over 11,000 people from both the sporting and non-sporting populations experiencing the injury each year in the UK.
’
Read More..Tweet it Now
"This research is particularly important for sportsmen and women of all levels and abilities," said Matthew Costa, Professor of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery at NDORMS, University of Oxford. "Achilles tendon rupture keeps people away from the sport for many months. For some, it stops them from ever returning to their favorite recreational activities, and for professional athletes, it can be a career-ending injury. Immediate mobilization in a brace is a safe alternative to plaster casting after an Achilles rupture, and patients report better early outcomes, probably because the brace allows them to walk earlier than the cast." Read More..
Some patients are treated with surgery, but non-operative treatment is increasingly preferred, with patients either being treated in a plaster cast to immobilize the foot and ankle or by the use of functional bracing that allows weight-bearing. However, before the UKSTAR study, there was little evidence towards which was more effective.
Although traditional plaster cast treatment protected the tendon as it healed, there were problems with casts including the immediate impact on mobility, additional risks associated with prolonged immobilization, and possible long-term issues arising from gait abnormalities and muscle weakness.
With the bracing method, there were questions around the safety profile, specifically whether the risk of re-rupture was higher, leading to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons being unable to recommend for or against functional bracing in their 2009 guidelines.
However, the study found that the risk of re-rupture of the tendon in bracing was lower than reported in the existing literature. Matthew Costa said: "Traditionally, patients with a rupture of the Achilles tendon are immobilized for several weeks in a plaster cast which restricts their mobility. However, our new research shows that immediate weight-bearing in a walking boot allows the tendon to heal just as quickly and with no increase in the risk of further rupture. Plus, the walking boot treatment is cheaper for the NHS."
Advertisement
The UKSTAR trial randomized 540 participants from 39 UK hospitals making it the largest study of its kind to compare the two treatments. Adult patients were randomly assigned to a plaster cast or functional brace. The objective was to compare function and pain, quality of life, complications including re-rupture, and resource use in patients having non-operative treatment. The study found no difference between the patient-reported Achilles Tendon Rupture Score (ATRS) at nine months, or in the rate of re-rupture of the tendon.
Advertisement