The Exoribonuclease is a proofreading enzyme that checks for mismatched nucleotides on the viral RNA and corrects them by removing them. In the same way, the ExoN enzyme removes the nucleoside analogs of the antiviral drugs and renders the treatment ineffective for diseases like HIV, HCV and Ebola.
‘ExoN enzyme acts as a proofreader that recognizes the errors in the virus RNA and corrects them during RNA synthesis.’
Tweet it Now
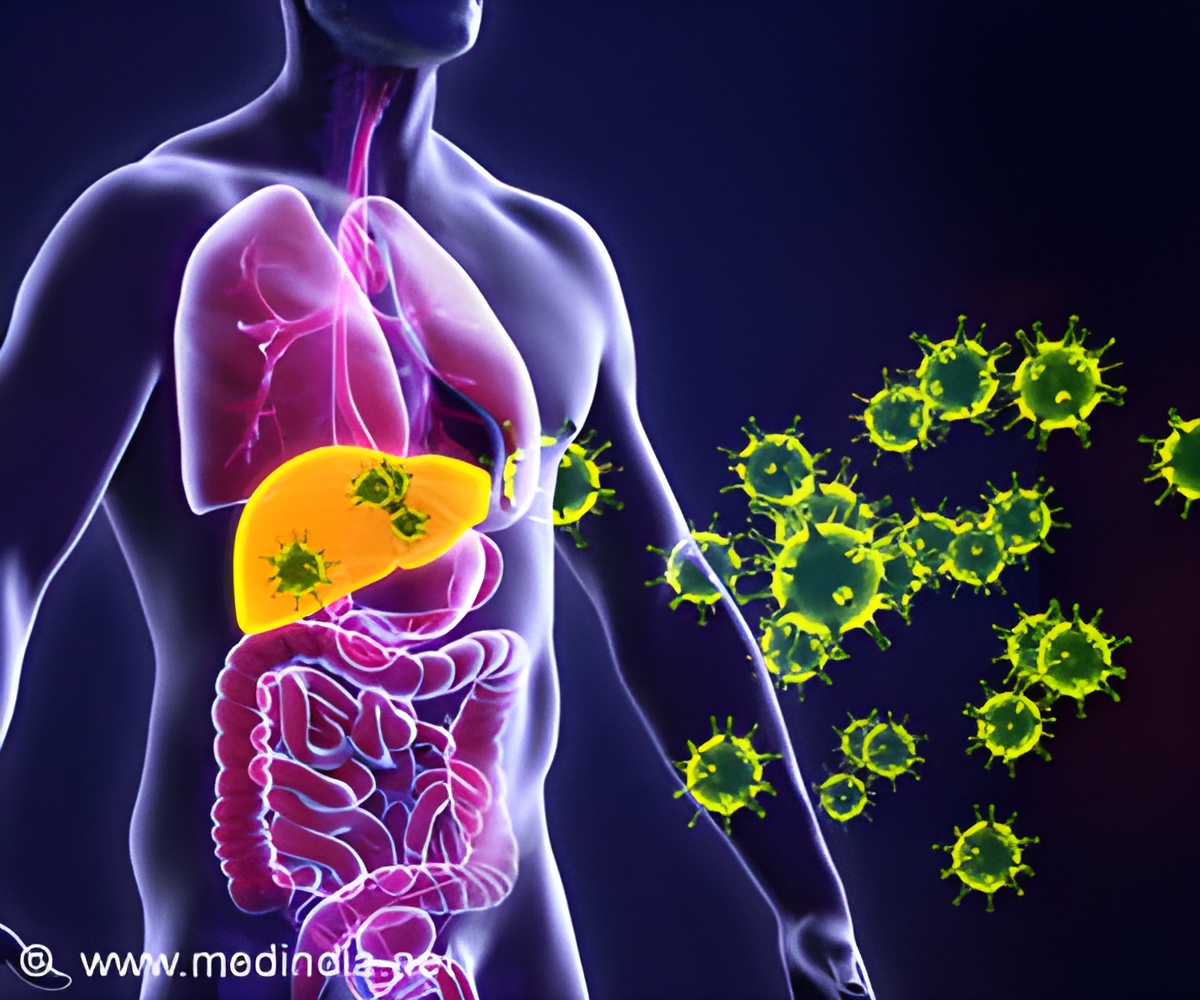
SARS-CoV-2 The SARS-CoV-2 is a single stranded RNA virus that causes Covid-19 infection. The genome of SARS-CoV-2 is larger compared to the other viral RNA, it creates a high number of errors during RNA synthesis. The ExoN enzyme proofreads it and corrects it before RNA synthesis. This enzyme is present only in few RNA viruses.
The Covid-19 infection has been declared a pandemic as it has affected many people in more than 180 countries. The virus mainly affects the upper respiratory tract and causes inflammation in the lungs leading to breathing problems. Severe infection can lead to death affecting other major organs like the heart, brain and kidneys. Treatment for this infection has been a challenge because of the presence of the ExoN enzyme which removes the nucleotides of the drugs and replaces it with the viral nucleotides during the translation process (RNA synthesis).
The structure of the ExoN enzyme was published in the Science journal.
According to Yang Yang- lead author of the study at the Iowa State University. “If we could find a way to inhibit this enzyme, maybe we can achieve better results to kill the virus with existing nucleoside antiviral treatments. Understanding this structure and the molecular details of how ExoN works can help guide further development of antivirals,”
The samples of the enzyme are preserved using the cryogenic electron microscopy technique. In this the samples are flash cooled to cryogenic temperatures in vitreous ice.The structure of the enzyme can be studied in detail and new antiviral drugs can be developed against the virus.
Advertisement