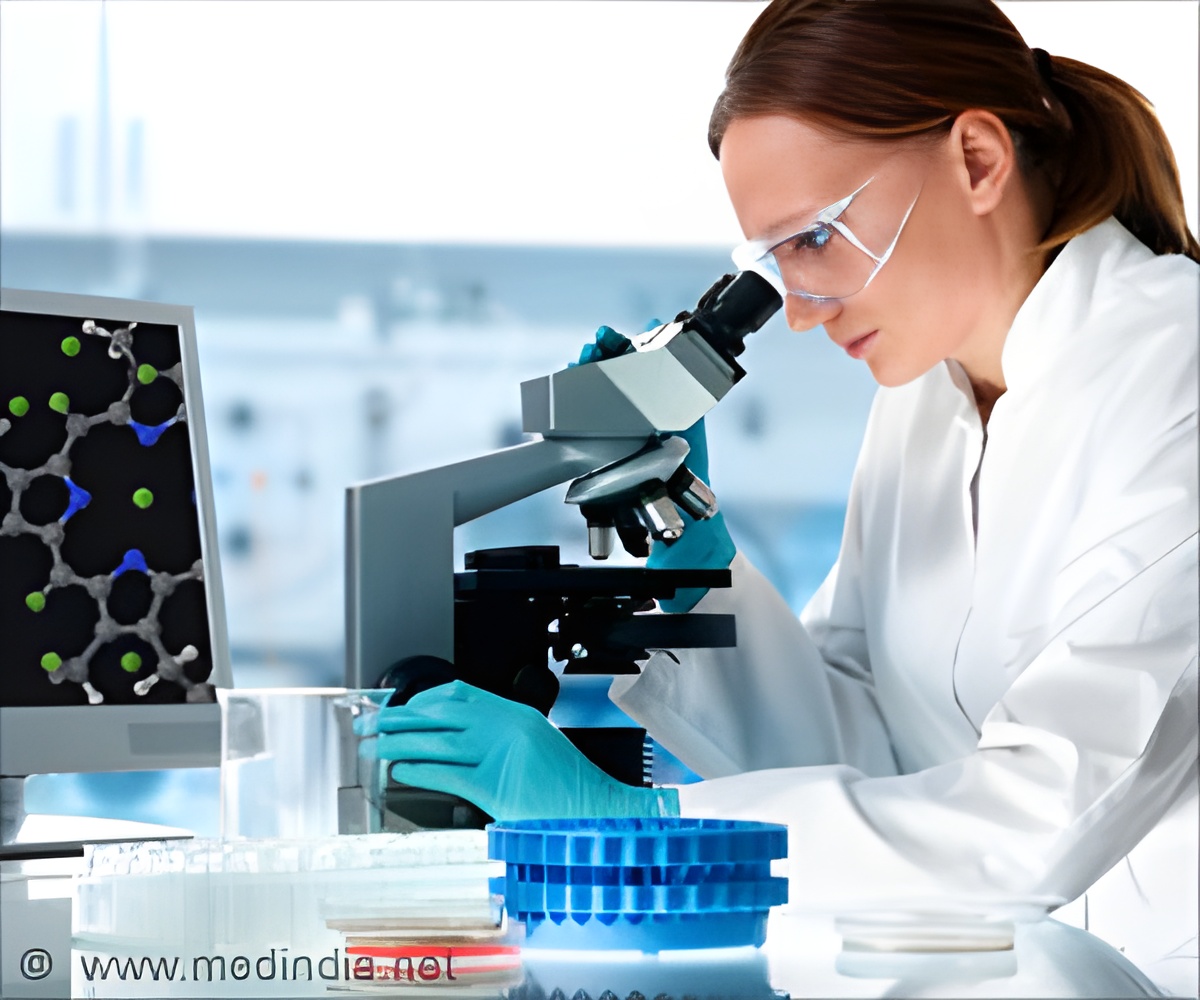
Researchers from NIST and three other institutions developed the new chip, which might be used to reduce the size and cost of some instruments that, like MRI, rely on nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The chip's sensitive internal detector boosts the response of microfluidic NMR on small samples and eliminates the need for the powerful magnets associated with larger NMR devices such as those used in MRI. The microfabricated chip could be mass produced and integrated easily with existing microfluidic systems.
"We envision this device being an element in a more complex microfluidic NMR system, maybe for medical diagnostics," NIST physicist and co-author John Kitching says.
The new device is related to NIST's chip-scale magnetometer** but has additional capabilities and different applications, Kitching notes. Like the older NIST device, the new chip uses rubidium atoms as magnetometers to detect the xenon polarization, but they also multitask. The novel design also uses the rubidium atoms to polarize the xenon atoms, boosting their NMR response, and mixes the two types of atoms in the same chamber at the detection stage, which enhances the signal strength 500-fold.
The device is housed in a silicon and glass chip about 3centimeters long with four small chambers connected by microchannels. In one chamber, circularly polarized light transfers angular momentum to the rubidium atoms' electrons. The rubidium atoms then exchange spin with the nuclei of the xenon atoms, enhancing their polarization and hence the NMR signal.
The polarized xenon and rubidium atoms then flow into a detection chamber. Thanks to the atoms' magnetic interactions the sensor can detect weak signals corresponding to fewer than 1 trillion polarized xenon atoms, a result competitive with low-field optical magnetometry.
Advertisement
Advertisement