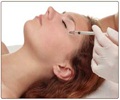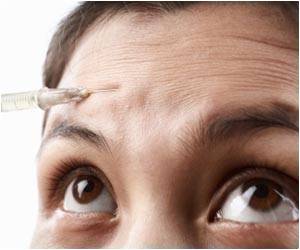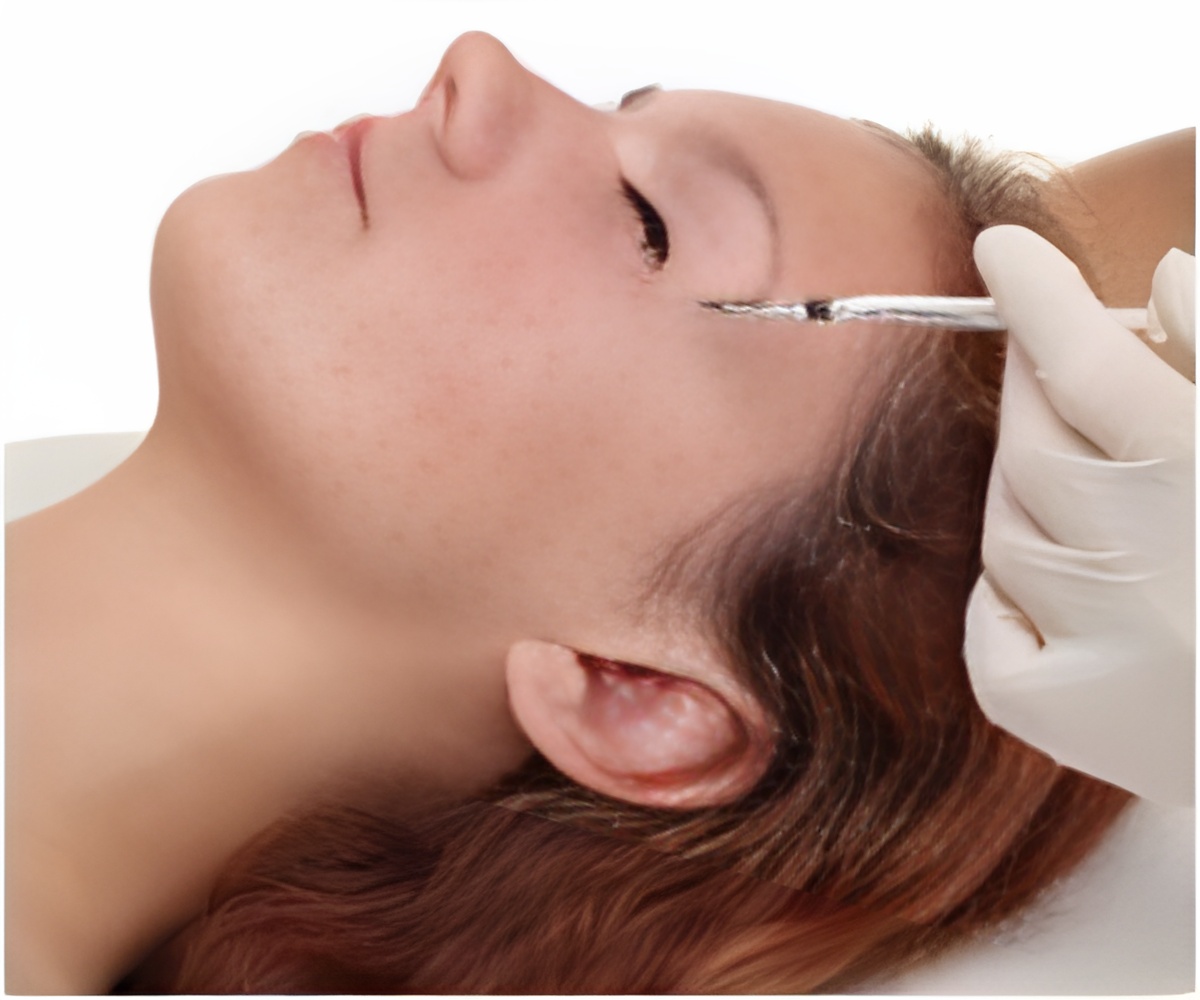
The study shows differing effects of local versus spinal injection of botulinum toxin and lends new insights into the molecular-level explanations for how "Botox" works to affect pain processing.
Botulinum toxin is most familiar from the use of BoNT-A, commonly known by the trade name Botox, for cosmetic plastic surgery. Both BoNT-A and BoNT-B are used for treatment of various neuromuscular disorders. Over the past decade, BoNT-A has been successfully used to treat certain chronic pain syndromes.
Since botulinum toxin causes temporary muscle paralysis, the pain-reducing effects have been attributed to muscle relaxation.
However, recent studies have suggested that other analgesic mechanisms may be operating as well.
Cellular-level studies showed that the two types of BoNT-B injection had differing effects in the pain-processing centers of the spinal cord.
Advertisement
The study is published in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
Advertisement