‘Newly developed artificial nose helps neurosurgeons to identify brain tumors during surgery and also enables a more precise removal of cancerous tissue.’
Tweet it Now
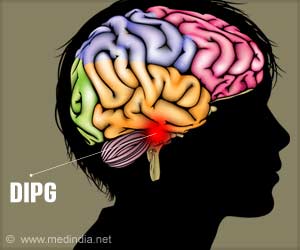
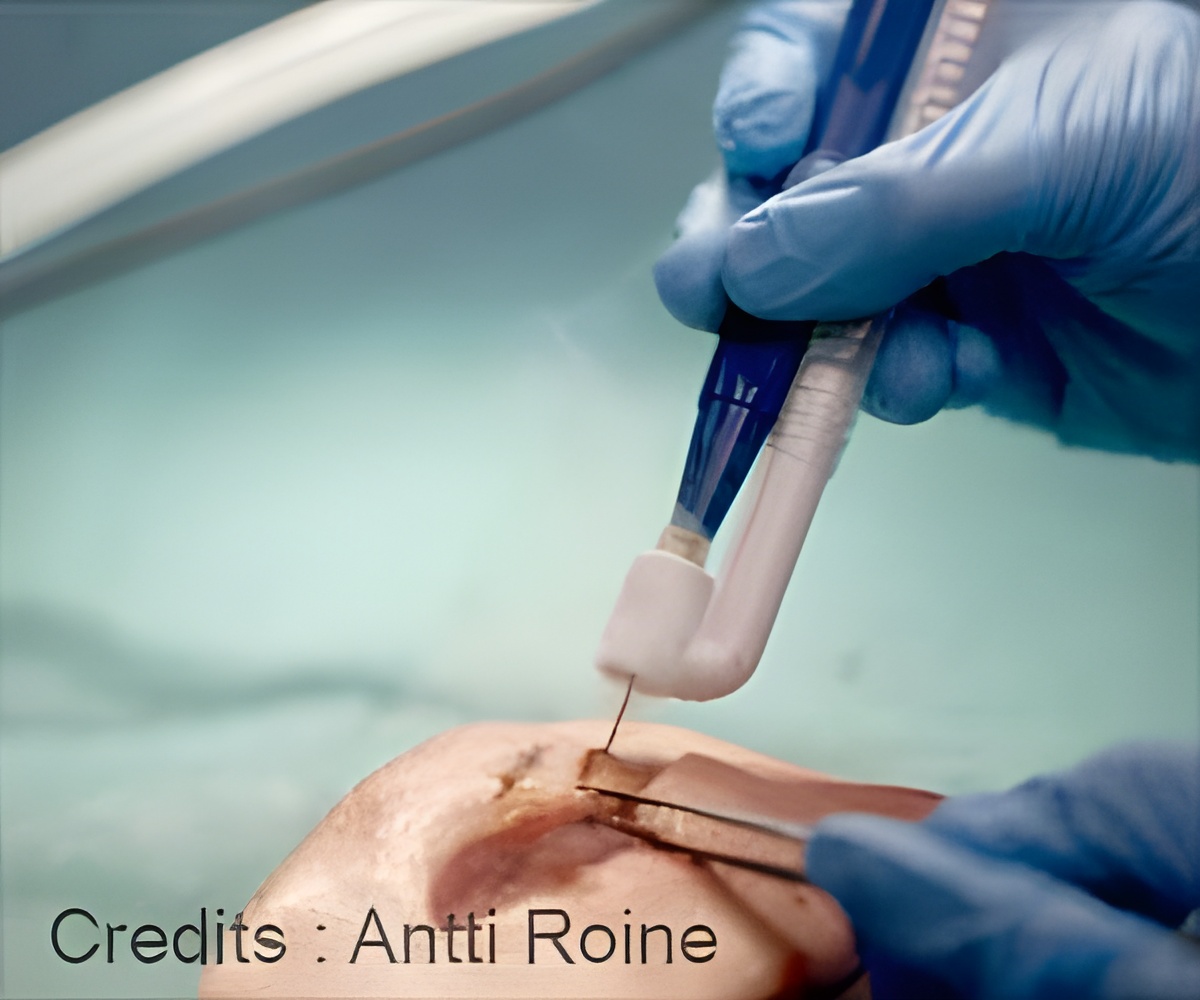
Electrosurgical resection using devices such as an electric knife or diathermy blade is currently a widely used technique in neurosurgery. When tissue is burned, tissue molecules are dispersed in the form of surgical smoke. In the method developed by researchers at Tampere University, the surgical smoke is fed into a new type of measuring system that can identify malignant tissue and distinguish it from healthy tissue.An article on using surgical smoke to identify brain tumors was recently published in the Journal of Neurosurgery.
"In current clinical practice, frozen section analysis is the gold standard for intraoperative tumor identification. In that method, a small sample of the tumor is given to a pathologist during surgery," says researcher Ilkka Haapala from Tampere University.
The pathologist undertakes a microscopic analysis of the sample and phones the operating theatre to report the results.
"Our new method offers both a promising way to identify malignant tissue in real time and the ability to study several samples from different points of the tumor," Haapala explains.
Advertisement
The technology is based on differential mobility spectrometry (DMS), wherein flue gas ions are fed into an electric field. The distribution of ions in the electric field is tissue-specific, and the tissue can be identified on the basis of the resulting 'odor fingerprint.'
Advertisement
The equipment used was developed specifically for the study. It consists of a machine learning system, which analyses the flue gas with DMS technology, and an electric knife, which is used to produce the flue gas from the tissues.
The system's classification accuracy was 83% when all the samples were analyzed. The accuracy improved in more restricted settings. When comparing low malignancy tumors (gliomas) to control samples, the classification accuracy of the system was 94%, reaching to 97% sensitivity and 90% specificity.
Source-Eurekalert