Their findings are being published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
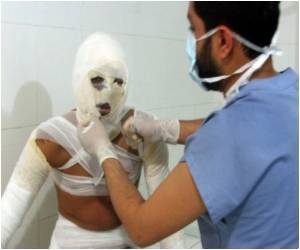
Otvos said that 40 percent of gowns and gloves in military hospitals are infected with Acinetobacter baumannii, and half of the soldiers returning from Iraq and Afghanistan with burn wounds will become infected.
Currently, these infections are treated with an antibiotic, either imipenem or colistin. However, both of these rapidly lose efficacy due to high rates of antimicrobial resistance. In addition, colistin is a strongly toxic drug and worldwide research is focusing on its replacement options.
For their study, the researchers used a strain of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from an injured Canadian soldier returning from Afghanistan for testing in the lab. They found that A3-APO, when given intramuscularly, was less toxic and more effective in reducing bacterial counts in the blood and the injury site than imipenem or colistin. The peptide also protected open wounds from environmental bacterial infection.
"This is the first peptide ever that is more efficacious in an animal model than anything else that is available," said Otvos, who hopes the peptide can be tested in clinical trials in the near future.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert