AI model predicts prostate tumor margins than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), revealed researchers.
Prediction and Mapping of Intraprostatic Tumor Extent with Artificial Intelligence
Go to source). In a series of tests, the AI model was found to be more accurate at predicting tumor margins than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), potentially improving the effectiveness of focal therapy, standardizing treatment margin definition, and reducing the chance of cancer recurrence.
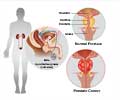
AI In Prostate Cancer
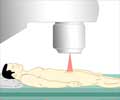
Focal therapy, a minimally invasive treatment approach used for localized tumors, is an alternative treatment for patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. The technique involves imaging guidance, such as MRI, to accurately locate the tumor and guide the treatment. Real-time imaging during the procedure helps monitor the treatment progress and ensures the precise delivery of energy to the intended area.‘The AI software helps surgeons, radiation therapists to enhance the results of focal ablation of prostate cancer. #prostatecancer #ai #prostatecancertreatment’





Current methods, however, can underestimate the extent of prostate cancer, complicating the definition of focal treatment margins. AI has the potential to better define these margins than MRI alone, a crucial factor in ensuring accurate diagnosis, precise treatment planning, and effective surgical procedures. METHOD
Working with scientists at Avenda Health, the team used biopsy data from multiple institutions to train the AI model, called Unfold-AI, to define margins during focal therapy. Testing was then conducted in an independent dataset of 50 patients who had radical prostatectomy for intermediate-risk cancer at the Stanford University School of Medicine. The team found the AI model was more accurate and effective at predicting tumor margins than conventional methods.
IMPACT
The advancement is an outgrowth of research initiated in 2009 by Dr. Leonard Marks, professor and deKernion Endowed Chair in Urology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
Advertisement
Reference:
- Prediction and Mapping of Intraprostatic Tumor Extent with Artificial Intelligence - (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666168323002550)

![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis](https://images.medindia.net/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)