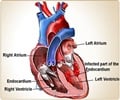
The first mathematical model in cardiology and emergency medicine to more quickly and reliably diagnose acute heart failure (AHF) in emergency room patients has been developed by researchers at St. Michael's Hospital. Research findings published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, have been shown to help physicians diagnose AHF with greater accuracy.
"In Canada, more than 100,000 people are hospitalized each year for acute heart failure while an estimated $1.4 - 2.3 billion is spent to manage the disease," explains Dr. Brian Steinhart, lead researcher and emergency medicine physician at St. Michael's Hospital. "Our model aims to ensure early correct diagnosis and treatment, which allows for shorter emergency department stay for these patients and could lead to improved health outcomes and better access to precious emergency department resources."According to researchers, the model uses natriuretic-peptide levels (a peptide hormone released from heart muscle to help regulate body fluids and blood pressure) and the clinician's judgement to help diagnose patients whose history, physical or chest X-ray may not clearly indicate AHF. Currently, accurate clinical diagnosis of AHF in the emergency department is less than 80 percent.
"In many cases, when a patient arrives in an emergency department complaining of shortness of breath, physicians are challenged to correctly diagnose patients," says Dr. Steinhart, "Our model does not require extensive clinical information, which makes it relatively simple-to-use. When the result is greater than 80 percent probability for heart failure, it suggests that the physician should treat for AHF and when it is less than 20 percent, the physician should be looking elsewhere for diagnosis."
The study developed the prediction model from the emergency department experience of 534 patients with undifferentiated shortness of breath enrolled in the Canadian Improved Management of Patients with Congestive Heart Failure (IMPROVE-CHF) trial.
Source-Eurekalert
RAS