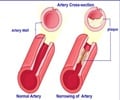
"Endothelial dysfunction has long been associated with an increased risk for coronary artery disease and cardiovascular events," says Virend Somers, a cardiologist at Mayo Clinic.
"Gaining a few pounds in college, on a cruise, or over the holidays is considered harmless, but it can have cardiovascular implications, especially if the weight is gained in the abdomen."
For the study, Dr. Somers and his team recruited 43 healthy Mayo Clinic volunteers with a mean age of 29 years. They were tested for endothelial dysfunction by measuring the blood flow through their arm arteries.
The volunteers were assigned to either gain weight or maintain their weight for eight weeks, and their blood flow was tested. The weight-gainers then lost the weight and were tested again.
Among those who gained weight in their abdomens (known as visceral fat), even though their blood pressure remained healthy, researchers found that the regulation of blood flow through their arm arteries was impaired due to endothelial dysfunction.
Advertisement
Dr. Somers says the study is unable to offer conclusions about whether recovery of blood flow is possible if the weight is kept on for several years.
Advertisement
"Physicians should know that the location of fat is important. Greater attention should be given to the circumference of a patient's waistline, not just their body mass index (BMI)." BMI is a formula that uses height and weight to estimate body fat and associated health risks.
The study was published in this week's Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Source-ANI