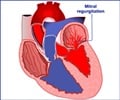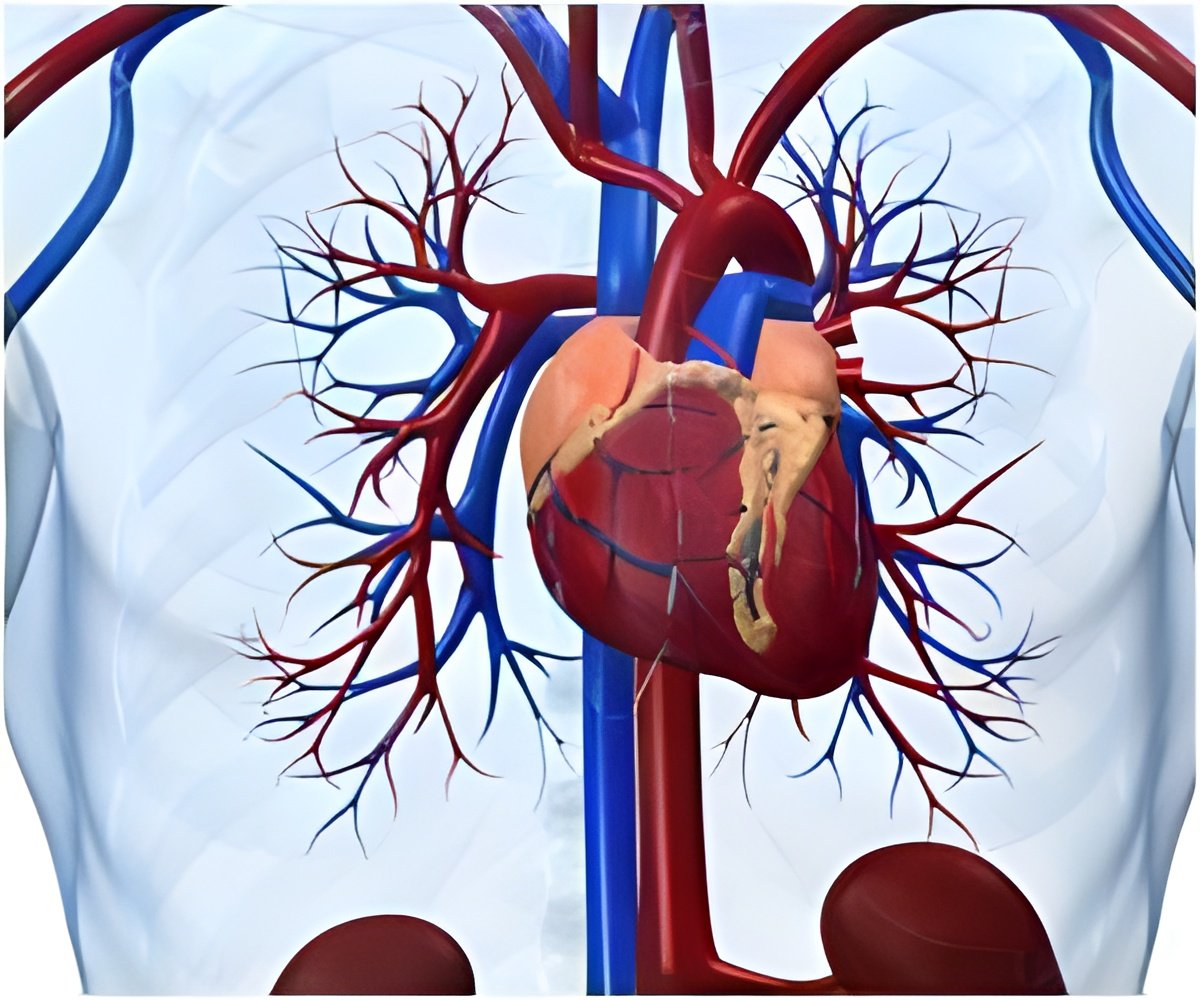
A new study finds that the anatomy of the heart's tricuspid valve can be used to predict the severity of leakage in the valve, which is a condition called tricuspid regurgitation. The study, conducted by researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, found that pulmonary arterial pressure, the size of the valve opening and papillary muscle position measurements could be used to predict the severity of an individual's tricuspid regurgitation.
"By being able to identify and measure an individual's particular tricuspid valve anatomical features that we have shown are correlated with increased leakage, clinicians should be able to better target their repair efforts and create more durable repairs," said Ajit Yoganathan, Regents' professor in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University.
The study was published in the January issue of the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging. Funding for this work was provided by the American Heart Association and a donation from Tom and Shirley Gurley.
Yoganathan and recent Coulter Department doctoral graduate Erin Spinner teamed with Stamatios Lerakis, a professor of medicine (cardiology), radiology and imaging sciences at Emory University, to non-invasively collect 3-D echocardiograms from 64 individuals who exhibited assorted grades of tricuspid leakage. Subjects included 20 individuals with "trace," 13 with "mild," 17 with "moderate" and 14 with "severe" tricuspid regurgitation. The subjects with "mild" to "severe" leakage exhibited a mix of isolated right, isolated left, and both right and left ventricle dilation.
From the 3-D echocardiography images of the heart they collected, the researchers measured (1) the area of the annulus, which is the fibrous ring that surrounds the tricuspid valve opening; (2) the distance between the annulus and the three right ventricle papillary muscles, which keep the valve shut when the ventricle contracts; and (3) the position of the papillary muscles with respect to the center of the annulus. The clinicians also measured pulmonary arterial pressure using standard clinical methods and assessed the grade of tricuspid regurgitation from "trace" to "severe" with color Doppler imaging.
Advertisement
"This study's use of advanced cardiovascular imaging, and more specifically 3-D echocardiography, provided new insight into the pathophysiology of tricuspid regurgitation and a good understanding as to why current surgical treatments for tricuspid regurgitation are not good enough," explained Lerakis. "I believe this study will change the focus and direction of future surgical therapies for tricuspid regurgitation only to make them better and more durable."
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert