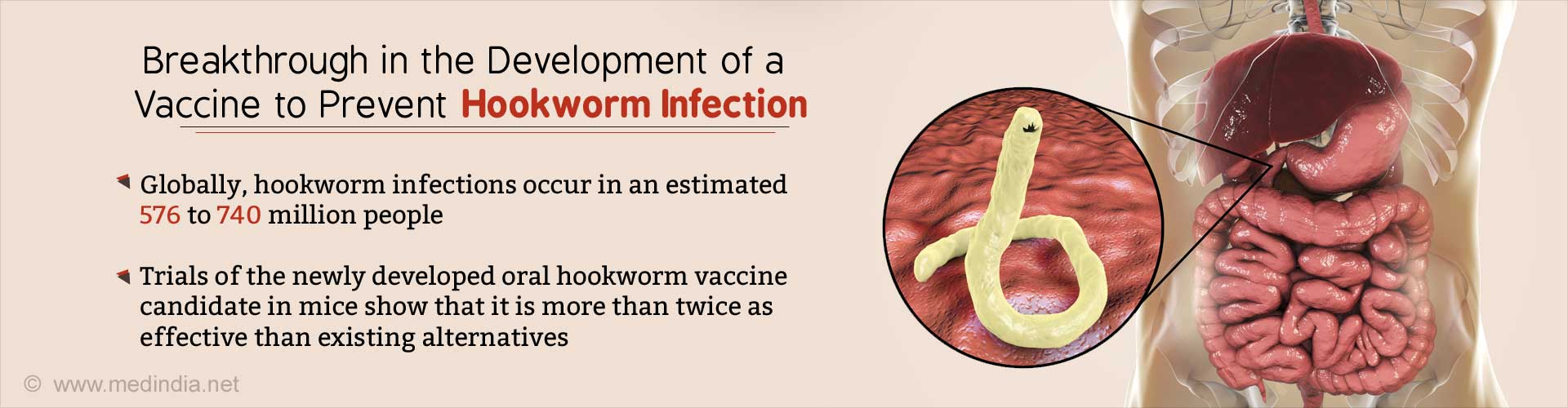
Hookworm is an intestinal parasite of humans. A polyhydrophobic amino acid (pHAA)-based oral hookworm vaccine candidate with major advantages developed.
Highlights:- Globally, hookworm infections occur in an estimated 576 to 740 million people
- A new polyhydrophobic amino acid (pHAA)-based vaccine candidate effective against hookworm infections developed
- The vaccine can be orally self-administered
Prof.IstvanToth (Chair in Biological Chemistry, School of Chemistry & Molecular Biosciences) and Dr.MariuszSkwarczynski (School of Chemistry and Biomolecular Sciences) from the University of Queensland Pharmacology have shared their insights on the recently developed oral peptide vaccine against hookworm infections.
‘Newly developed oral hookworm vaccine is a change maker in field of medicine.’
Read More..




Advertisement
What are the traditional vaccines used against hookworm infections?
-
Early hookworm vaccines for veterinary purposes utilize whole parasite larvae-based approaches, which are shown to be not safe.
-
Traditional vaccines are typically injectable, so it is not possible to use hookworm parasite (1 cm in size).
-
Recombinant forms of larval antigens, e.g., Ancylostoma secretory protein-2 (ASP-2), cause strong allergenic responses in vaccinated human subjects.
Advertisement
How is the oral hookworm vaccine different from traditional vaccines?
- The newly developed polyhydrophobic amino acid (pHAA)-based vaccine candidate has major advantages.
- The hookworm vaccine is peptide-based and do not use whole pathogen/microbe as the vaccine material.
Advertisement
Advantages of oral hookworm vaccine
- It uses only minimal antigenic fragment (p3) of a pathogen protein (APR-1) therefore there is no risk to induce allergic responses, which was reported previously in hookworm vaccine trials in humans.
- This vaccine does not need an adjuvant (immune stimulator), which enhances vaccine safety, as adjuvant can cause side effects.
- The vaccine is not only effective upon injection, but effective after oral administration.
- The vaccine is stable and cheap.
How oral hookworm vaccine reduces worms?
-
The alternate vaccine reduced the number of worms by 30% to 40%, whereas the newly developed oral peptide vaccine decreases worms by 94% based on PHAA-p3.
-
The current studies are performed on mice. Further studies are planned on hamster and dogs.
-
The vaccine is peptide-based, so it is stable in normal storage and transport environment.
-
The exact timespan and temperature range will be determined in the future.
Oral hookworm vaccine trial on humans
-
Hookworm vaccines do not need to achieve sterilizing protection, i.e., 100% worm reduction, as 80% worm burden reduction in humans is modelled to have a highly positive impact in hookworm-epidemic areas.
-
Moreover, hookworm-related morbidity is directly linked to infection intensity, and controlled, low-burden experimental human hookworm infection is well tolerated and has even been shown to carry some health benefits in humans.
-
Thus, the vaccine candidates are highly promising and should be progressed to human testing.
Source-Medindia