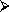 Tobacco legislation is available in all most all member countries, five have alcohol legislation, two have for diet and nutrition, only one has for physical activity.
Tobacco legislation is available in all most all member countries, five have alcohol legislation, two have for diet and nutrition, only one has for physical activity.
 Legislative support for other risk factors is yet to be fully developed in Member countries.
Legislative support for other risk factors is yet to be fully developed in Member countries.
 Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is the first legally binding international treaty to reduce harm due to tobacco, which has been established by WHO.
Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is the first legally binding international treaty to reduce harm due to tobacco, which has been established by WHO.
 Except Indonesia, all member countries have authorized the WHO FCTC and are implementing the various elements of MPOWER — a package of six effective tobacco control policies.
Except Indonesia, all member countries have authorized the WHO FCTC and are implementing the various elements of MPOWER — a package of six effective tobacco control policies.
 By increasing tobacco taxation, Thai Health Promotion Foundation (ThaiHealth) has played a crucial role in NCD prevention and control in Thailand.
By increasing tobacco taxation, Thai Health Promotion Foundation (ThaiHealth) has played a crucial role in NCD prevention and control in Thailand.
 A steady decrease in smoking prevalence has been seen among adults due to consistent increase in taxes, similar taxation is needed to reduce the demand for other unhealthy products.
A steady decrease in smoking prevalence has been seen among adults due to consistent increase in taxes, similar taxation is needed to reduce the demand for other unhealthy products.
Status of implementation of Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in South-East Asia Region, 2011

 Bangladesh is the first country in the Region to establish a National Tobacco Control Cell (NTCC) under the Bloomberg Initiative and it has mobile courts to enforce tobacco control law across the country and take action of violations of the law.
Bangladesh is the first country in the Region to establish a National Tobacco Control Cell (NTCC) under the Bloomberg Initiative and it has mobile courts to enforce tobacco control law across the country and take action of violations of the law.
