What are the Causes of Foul Smelling Stool?
The major causes of foul smelling stool include the following:
Overeating: When we overeat, more than the body can digest, it causes indigestion. The undigested or partially digested food are acted upon by the bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract causing bloating, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and excessive odorous flatulence indigestion can therefore cause the stool to smell really bad.

Diet:
- Sulphur containing foods: Consuming excess of sulfur-containing foods can cause the stool to stink. Sulfur is an essential mineral and so it must be included in the diet in appropriate amounts. Some sulfur-rich foods include the following:
- Eggs
- Garlic
- Legumes
- Dried fruits
- Cruciferous vegetables – cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, bok choy, radish, turnips, German turnip (kohlrabi)
- Dairy products except for butter
- Processed foods: Processed foods contain synthetic substances and additives that cannot be digested and can lead to foul-smelling stool
- High fat diet: Diet rich in fat may be improperly digested due to insufficient amounts of the enzyme lipase necessary to digest fat. The undigested fatty food rots as it travels down through the digestive tract and causes the stool to stink
- Dairy foods / lactose intolerance: Consuming dairy foods excessively or having deficiency of lactase, an enzyme necessary to digest the lactose in dairy products, results in undigested lactose accumulation in the intestine. This is acted upon by bacteria resulting in bloating, abdominal pain and discomfort, diarrhea, and foul smelling stool
Excess Antibiotic Use: Excess use of antibiotics can alter the gut microbial flora and result in the overgrowth of bad bacteria which can cause smelly stool
Gastrointestinal Tract Infections: Infections of the digestive tract with bacteria (Salmonella typhi, Shigella dysenteriae, Escherichia coli), viruses (Norovirus, Rotavirus) or parasites (Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia) can cause inflammation of the intestine, accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea and foul smelling stool
Excessive Vitamin Supplementation: Excess intake of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K can result in foul smelling stool
Malabsorption: When there is malabsorption, the body is unable to absorb the ingested food, and the unabsorbed food remains in the intestine and is acted on by intestinal bacteria resulting in foul smelling stool. Medical conditions associated with malabsorption include celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis), surgical removal of bowel, food allergies and intolerance
Miscellaneous Causes: Other causes include chronic pancreatitis, resulting in lipase deficiency and cystic fibrosis, which also causes insufficiency of pancreatic secretions
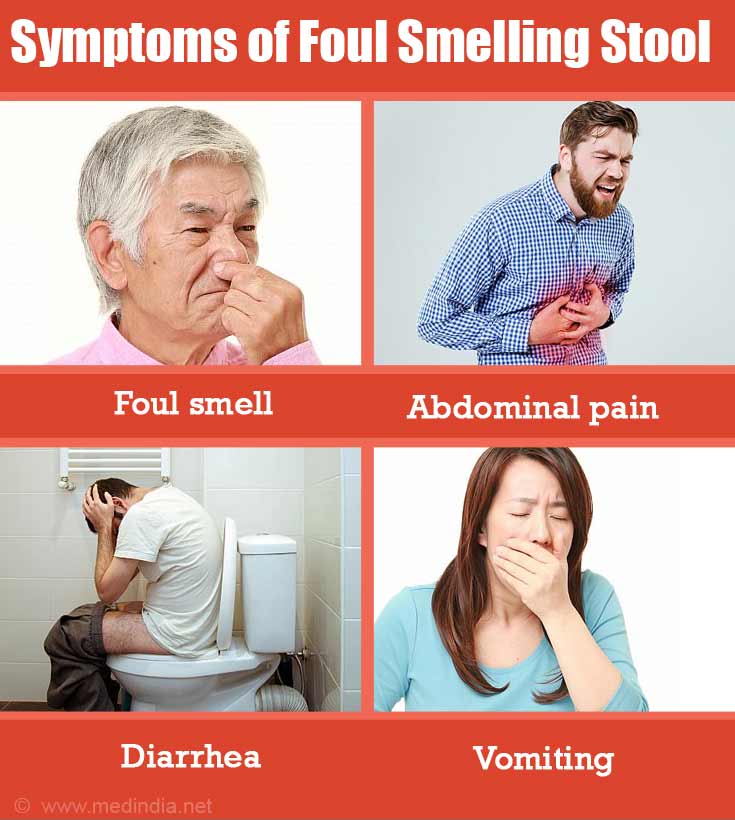
What are the Symptoms Associated with Foul Smelling Stool?
The primary symptom is the ‘foul smell’ itself. Other symptoms that can occur depend on the cause and can include the following which may give a clue to the diagnosis:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
| Abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence and diarrhea | Indigestion, malabsorption, lactose intolerance |
| Severe watery diarrhea with mucus or blood associated with fever and abdominal pain and vomiting | Bacterial or viral infections |
| Bloody diarrhea, fever and abdominal pain | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Black tarry stool (melena) | Bleeding in the upper digestive tract |
| Unintended weight loss | Inflammatory bowel disease, malabsorption |
Depending on the patient’s history and clinical examination findings, further tests including blood tests, stool tests, upper and lower bowel endoscopies and imaging studies may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis