Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the science that focuses on equipment design at workplaces with a view to reduce fatigue and discomfort in workers by improving working conditions.
Ergonomics is the science that shapes jobs, equipments or work places in such a way as to make it more worker-friendly.
Ergonomics is derived from the Greek words ‘ergon’ (work) and nomos (law). Ergonomics or Human Factors or Human Engineering is a field that explores ways to understand and improve human capabilities in their interaction with machines and the environment. The aim of ergonomics is to design machines, appliances, work systems and tasks in such a way that they guarantee human safety, comfort and health and improve work performance.
Human beings are the focus of ergonomics. The field of study tries to eliminate unhealthy, unsafe, uncomfortable or debilitating situations at work or in everyday life with findings based on the physical, psychological abilities and limitations of human beings.
Ergonomics in the workplace
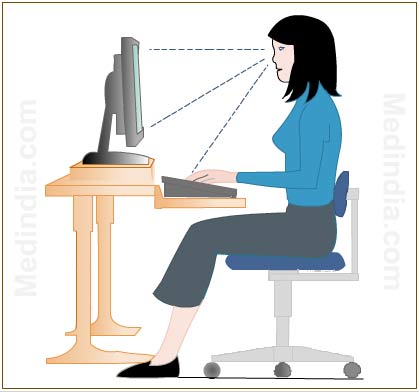
In general parlance, ergonomics refers to physical ergonomics relating to workplace as in ‘ergonomic chair’, ‘ergonomic keyboard’ and ‘ergonomic mouse.’ Ergonomics in workplace deals with the short term and long term safety of employees. It aims to improve safety at workplace thereby reducing costs to company paid out as compensation to workers. Statistics show that over 5 million workers sustain overextension injuries each year in the US. Experts in the field of ergonomics hold that they can design workplaces that can prevent overextension in workers and thus save billions in workers’ compensation in computer related industries.
Applying ergonomics in workplaces involves the reactive or the proactive approach. Reactive ergonomics is the corrective action that is taken after the damage is done—altering or fixing things at a workplace after injuries have been reported. Proactive ergonomics explores areas that need fixing or improvement before the problem of discomfort for workers develops into mammoth proportions. Equipment design or task design techniques are employed to fix problems. In Equipment design, the actual physical devices - chair, table, computers etc, used by people are modified if they are not user-friendly. Task design changes focus on improving the tasks that people do with the physical devices—computers, in this case. Environmental design makes changes in the work environment such as channel music and controlled room temperature.
Engineering Psychology
This is an interdisciplinary subject under ergonomics that studies human-machine interaction with the view to improve the relationship. An engineering psychologist tries to make the interaction more user-friendly by re-designing equipment, altering the way in which people use machines or changing the location of work to increase productivity.
People who work on the computer for long hours need to realize the body is sedentary during that time with no chance of physical workouts. While being engrossed in work we even forget to blink our eyelids sometimes. Ergonomics training is catching up at workplaces in advanced countries because more and more people are waking up to the occupational hazards of getting so addicted to technology. It is important for a computer user to know which is the right sitting posture for that kind of job, the correct position to use the hands while working on the computer, how to move the elbows and shoulders, how to take care of the back and how to do relaxation techniques for the eyes.
Ergonomic furniture and ergonomic accessories are becoming increasingly popular in markets all over the world. For instance, ergonomic keyboards designed with a view to reduce muscle strain and repetitive stress injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome, are hitting the market offering different features. Some ergonomic keyboards a single board with keys arranged in 2 or 3 groups at different angles rather than a straight keyboard. Some have the keyboard split into separate independent pieces with elevated sections at different angles. Some ergonomic keyboards have keys fixed at a vertical elevated level so that the user’s hands can be unbent and perpendicular to the ground.
An undulating chair, a vibrating mouse and movable arms for monitors are some of the new ergonomic products getting ready to hit the market soon. Health experts opine that more than these fancy gadgets, it is ergonomics training that will benefit the workers more and prevent computer-related health hazards.