When is PSA test done & Screening for Prostate Cancer
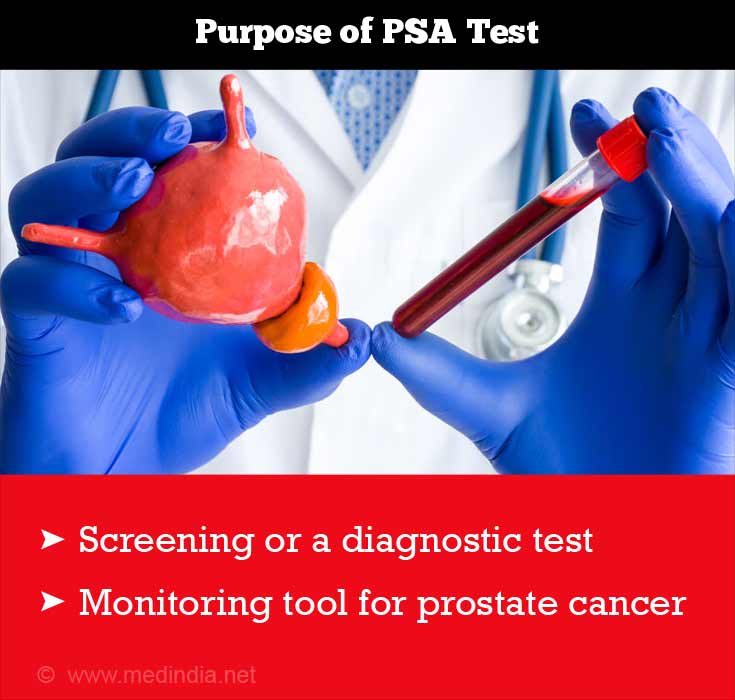
PSA test has two different purposes – one for screening and the other for monitoring of prostate cancer
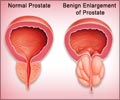
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the USA recommends the use of the PSA test, in conjunction with a digital rectal exam (DRE) to help diagnose prostate cancer in men above the age of 50 years, who do not show any symptoms of the cancer.
During DRE, the doctor inserts a gloved finger through the rectum and feels for bumps or other abnormalities along the rectal wall near the location of the prostate.
The PSA test is used for two different purposes.
It can be used as a screening or a diagnostic test in men who are not yet known to have cancer. If the screening value shows values greater than 4.0ng/ml, it may evoke suspicion. Values above 10.0ngms/ml could be indicative of cancer.
When PSA test is used as a monitoring tool in those who already have diagnosed disease, the increased PSA values could be indicative of disease, or of recurrence after an initial successful treatment, such as surgery. Elevated PSA could be the first sign of a cancer ‘comeback’ in such patients even in the absence of other clinical symptoms although it may not be true for all cases.
It must also be noted that a single elevated PSA value may not be enough to indicate cancer and a repeat of the PSA test after a month may be necessary to arrive at the correct diagnosis.
Screening for Prostate Cancer:
In USA PSA test is normally recommended for men over the age of 50 years although some doctors advocate its use to screen men over 40 years; however this remains controversial. Whatever the case, it is advisable to inform the individuals about the risks, limitations and benefits involved in PSA screening before using it.
In any national screening programme - screening for prostate cancer using PSA in men above 50 years is not considered cost effective. However in certain individuals where the risk is relatively higher the role of PSA as a screening tool is undisputed. These include:
- Family history -those with a father or brother who had prostate cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease
- Race - men of African-American origin are at a greater risk of developing prostate cancer than Caucasians, Asians or Native Americans
Suggestions like increasing the age to 65 years instead of 50 years may also make screening cost effective as Prostate cancer occurs most frequently in older men, with 63% of the disease occurring in men over the age of 65 years.

![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis](https://images.medindia.net/patientinfo/1920_500/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)