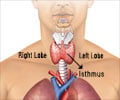
Q: Which doctor treats goitre?
A: Goitre is treated by an endocrinologist. The patient may be referred to a surgeon if surgery is needed.
Q: What is colloid goitre?
A: Colloid goitre or adenomatous nodules is prevalent in areas of iodine deficiency (endemic goitre). It affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 50 years and women more often than men. Large goitres hinder breathing and occasionally obstruct swallowing.
Q: What is the difference between simple and toxic goitre?
A: Simple goitre is a noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid gland. Unless there is severe iodine deficiency, the glandular function is normal and patients do not experience symptoms. Toxic multinodular goitre or toxic nodular struma or Plummer''s disease is associated with hyperthyroidism and starts from a prevailing simple goitre. It is rare in children, but very common in older women.
Q: What are the leading causes of goitre?
A: The leading cause of goitre is known to be dietary iodine deficiency which is often noted in mountainous areas or inlands far away from the sea.
Q: Are goitres cancerous?
A: Goitre can be a result of thyroid tumors which are usually benign. There are several kinds of thyroid cancer that can cause swelling of the thyroid gland.