- Shortness of Breath. Bozkurt B and Mann DL. Circulation. 2003;108:e11-e13
About
Dyspnea is a condition that leaves us breathless, literally! Sudden onset of breathlessness could be a medical emergency and should be immediately treated.
Breathing is one of the most important vital functions of the body- we are alive so long as we breathe. Difficulty with breathing therefore could lead to panic.
We breathe through the respiratory tract which consists of the nose, trachea or windpipe, the bronchi, the smaller bronchi or bronchioles and the airsacs. The exchange of gases i.e. oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place at the level of the thin airsacs called alveoli. The rhythm of inhaling and exhaling is maintained by the respiratory center in the brain through nerves supplying the respiratory tract. The muscles of the chest and abdomen assist in breathing, especially if the person requires taking deeper breaths.
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea as it is medically termed, could result due to a number of causes, which are not necessarily limited to the respiratory tract. Excessive exhaustion, extremes of temperatures or travelling to high altitudes could cause temporary shortness of breath. If the problem persists and is not relieved by rest, it is likely to be due to an underlying medical problem. Listed below are some of the medical causes of dyspnea:
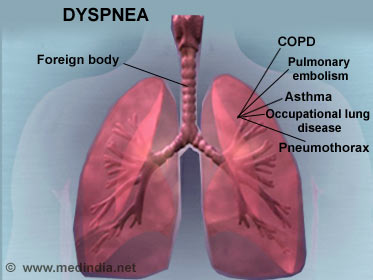
Respiratory Causes: Conditions affecting the lungs and the respiratory tract are most commonly associated with shortness of breath. These include:
- Infection: Infection of the bronchi (bronchitis) and lungs (pneumonia) are commonly associated with shortness of breath. The patient may show the presence of symptoms like cough, white or yellow colored sputum, and fever. The diagnosis may be confirmed through an x-ray of the chest.
- Asthma: Asthma is a recurrent condition where the smaller airways narrow in response to certain stimuli like cold air or a viral infection, resulting in difficulty with breathing. The patient feels better on sitting down than while lying. Wheezing is present when the patient breathes out. The patient gives a history of similar episodes in the past, which have reduced with anti-asthma medications.
- Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD): COPD includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis usually affects smokers and is characterized by the presence of a chronic cough with sputum production. Emphysema is also seen in smokers and is diagnosed on x-ray.
- Occupational lung disease: Exposure to substances like silicon or asbestos in the workplace can damage lung tissue and result in shortness of breath. In some cases, the patient may develop cancer due to exposure to these substances. It is therefore necessary to evaluate these cases early and reduce exposure as soon as possible.
- Pulmonary embolism: Pulmonary embolism is a condition where a clot usually from the legs travels to the lungs. It results in sudden shortness of breath with pink colored frothy sputum and sometimes chest pain. The patient may have undergone recent surgery, may have been bedridden in the recent past due to some health issue, or may be on medications like estrogens. The condition is a medical emergency and warrants immediate treatment.
- Foreign body: The presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract should be suspected in a child complaining of sudden breathlessness.
- Lung cancer: Lung cancer can result in shortness of breath. Other symptoms include cough, weight loss, and coughing up of blood. The patient often gives a history of smoking.
- Pleural effusion: Pleural effusion is a condition where the area outside the lungs gets filled with fluid. The fluid restricts the breathing of the patient, resulting in shortness of breath. The condition can be diagnosed on examination.
- Pneumothorax: Air may get into the area surrounding the lungs during chest trauma; this condition is called pneumothorax. The air does not allow free expansion of the lungs and results in shortness of breath. The breathlessness is sudden and should be treated as a medical emergency.
Other causes that result in shortness of breath are:
- Cardiac causes: Heart failure causes shortness of breath; the difficulty with breathing is more prominent when the patient lies down. The patient may get up in the night with coughing. Shortness of breath is also observed with increase in activity. In addition, swelling at the ankles may be present. A heart attack may also cause breathlessness. The patient may complain of chest pain that radiates along the left arm. An ECG or echocardiogram may help to diagnose a cardiac cause of breathlessness.
- Condition affecting the blood: Anemia is a condition where the red blood cell count is extremely low. The patient may breathe faster to meet the oxygen requirements of the body. Conditions like diabetes, uremia, methmoglobinemia and carbon monoxide poisoning could affect the pH of the blood, thus resulting in shortness of breath.
- Conditions affecting the nervous system: Since respiration is controlled by the brain, conditions that affect the respiratory center in the brain like stroke or trauma could affect breathing. In addition, conditions that affect nerves that result in muscle weakness like myasthenia gravis and Guillian Barre syndrome could result in weakness of the respiratory muscles, thus resulting in breathlessness.
- Psychogenic cause: A psychological cause like anxiety can cause a person to breathe faster and complain of shortness of breath. Panic disorder is also a common cause of shortness of breath.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which doctor should I visit in case I suffer from breathlessness?
You should visit your general practitioner or family doctor in case you suffer from breathlessness. If the breathlessness is sudden in onset, you should visit the emergency without delay.
2. How is shortness of breath diagnosed?
Shortness of breath is diagnosed based on the symptoms and examination of the patients. Tests like chest x-ray or spirometry may be asked for if a lung cause is suspected. An ECG or an echocardiogram helps to rule out a cardiac cause. Other tests depend on the possible cause of breathlessness.