Treatment of Ascites
The SAAG is helpful for therapeutic decision making.
If the SAAG is low (Non-portal hypertension related ascites)
- The Ascites may be due to cancer like ovarian malignancy.
To treat it, surgery and chemotherapy are recommended
Diuretics are given for the peripheral fluid accumulation.
Therapeutic paracentesis (draining the ascitic fluid from the abdominal cavity using a needle) is done.
- Tuberculous peritonitis
This is treated with antituberculous therapy.
- Nephrogenous dialysis
Vigorous dialysis is given.
- Pancreatic ascites
Procedural intervention is done or spontaneous resolution is seen.
- Chlamydia peritonitis
Doxycycline therapy is prescribed.
If the SAAG is high (Portal hypertension-related ascites)
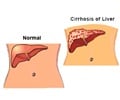
Cirrhosis of liver is the most common cause and the underlying liver disease is to be addressed first. The patient has to be counselled to give up alcohol.
First line of treatment
1. Diet
Dietary sodium restriction is necessary in portal hypertension-related ascites as fluid loss and weight change are related to sodium balance in the body. It is not the water intake but the sodium intake which causes the fluid build-up. Hence, it is very important to restrict the sodium intake to 2000mg/day (1 teaspoon). There should be coordination between the dietician and the patient’s family to prepare a diet chart and follow it at home.

2. Diuretics
Spironolactone is the mainstay diuretic in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. In general, spironolactone and furosemide are combined with a sodium-restricted diet and this is effective in over 90% of patients. The dose of diuretic medication is adjusted till best results are obtained.
3. Antibiotic Therapy
A high level of suspicion for bacterial infection is appropriate and empirical antibiotics should be started whenever required.

Second line of treatment
This is required in refractory ascites when the patient does not respond to salt-restricted diet and diuretics. Less than 10% patients are refractory to standard therapy.
It includes-
- Therapeutic paracentesis- Draining fluid from the abdomen using a needle under sterile conditions is called paracentesis or abdominal tapping.
Paracentesis only relieves the symptoms but does not correct the underlying cause.
It can be large volume paracentesis (6-10 litres) for therapy in cirrhosis or small volume paracentesis (1-2 litres) for relief of dyspnoea in tense ascites. Large volume paracentesis is followed by albumin infusion.
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt)- A procedure performed through the veins to place a shunt in the liver to improve the blood flow.
Besides refractory ascites, it is done when simpler methods to control bleeding from varices do not succeed.
- Liver transplantation is required in some cases.