- The Role of the Skin Barrier in Occupational Skin Diseases. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26844905)
- 10 Signs of Poor Skin Health – With Cures & Treatments - (https://www.brainz.org/10-signs-poor-skin-health/)
- All About Rosacea - (http://www.rosacea.org/patients/all-about-rosacea)
- Anatomy of the Skin - (https://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/anatomy/)
- Hormonal factors key to understanding acne in women - (https://www.aad.org/media/news-releases/hormonal-factors-key-to-understanding-acne-in-women)
- Pathological mechanisms of acne with special emphasis on Propionibacterium acnes and related therapy. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12926793)
- Psoriasis Resource Center - (https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/scaly-skin/psoriasis)
- Vitiligo - (https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/vitiligo)
- Hives - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000845.htm)
- Hives (Urticaria) - (https://acaai.org/allergies/types-allergies/hives-urticaria)
About
The skin is the mirror of health and these 10 most common skin disorders can be physically as well as emotionally daunting, as a glowing skin is an important aspect of physical beauty.
The body’s internal organs are contained within the confines of the skin and the skin color, texture and radiance are key factors in defining an individual’s physical appearance.

Anatomy of the Skin
The skin is a vital and complicated organ that covers the entire body, making it the largest organ. The skin is 2mm in thickness and 6 pounds in weight.
Types of Surface Skin
The skin is of two types:
- Thin and hairy: This type of skin is found in most parts of the body.
- Thick and hairless: This type of skin is found in those parts of the body that are used extensively, with a lot of friction involved, like on the soles of the feet and the palms of the hand.
Layers of Skin
The skin consists of three layers:
A) Epidermis: This is the outermost layer of the skin and consists of melanocytes that determine the color of the skin. The thickness of the epidermis varies from site to site, with the thickness of the palm being 1.5 mm while the eyelids are 0.5mm. The epidermis consists of different layers of:
- Basal cells: These cells are also called the stratum germinativum. The basal cells constitute the lower most layer of the epidermis and are constantly dividing. When newer cells are formed, the older cells are pushed to the top, after which they are slowly shed. The basal cells also contain melanocytes which give rise to melanin. The dark pigment gives color to the skin, whether dark brown or brown. Age spots (solar lentigines) and birth marks are areas with high concentration of melanin.
- Squamous cell layer: This cell layer is present above the basal layer and the cells are packed together with projections that seem spiny. The cells from the basal cell layer that mature are slowly pushed up to the squamous cell layer are called squamous cells. This layer also contains keratinocytes which produce keratin, found in skin, hair and nails.
- Stratum granulosum: As the basal cells and the keratinocytes move up into the stratum granulosum, they are flattened, grow bigger and stick to each other. This results in durable skin cells that are toughened. The cells continue to migrate slowly upward towards the last and the fourth layer of the epidermis.
- Stratum corneum: This is the outermost layer of the skin and consists of dead cells.
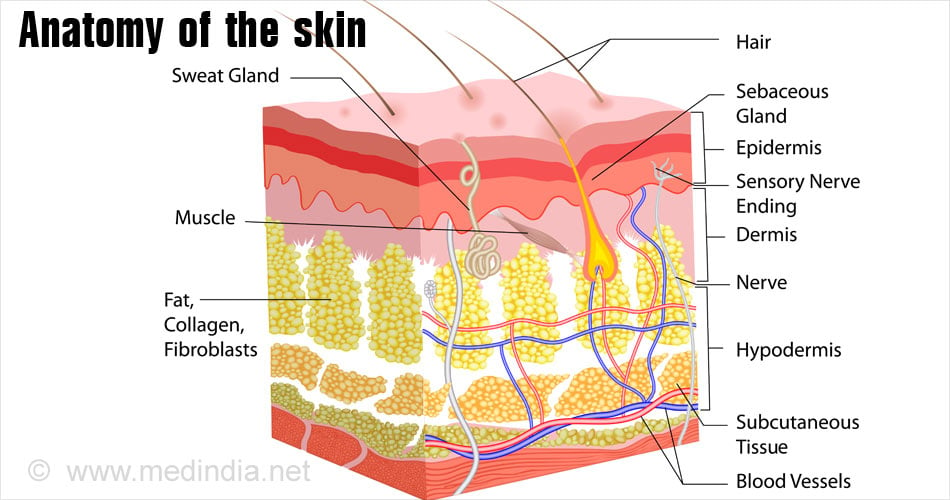
B) Dermis: The dermis is the second layer, found just below the epidermis. The dermis consists of hair follicles, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerve endings, oil and sweat glands. The dermis has two layers:
- Papillary layer: This layer is the upper layer of the dermis and consists of the collagen fiber. The functions of the papillary layer are:
- Temperature regulation
- Supply of nutrient to specific layers in the epidermis
- Reticular layer: The collagen fibers are more in this layer and are thicker. The cells are parallel to the skin surface. Their functions include:
- Gives elasticity
- Provides strength
- Aids in structure building
C) Subcutis or Hypodermis: This layer is below the first two layers and is a fatty layer of subcutaneous tissue. They consist of fat cells and collagen cells. Hair follicles, sweat glands, blood vessels and nerve cells pass through this layer. The thickness of this layer varies from site to site and also from one individual to another. The functions of this layer include:
- Insulation: Conservation of body heat
- Shock absorption: Protecting the internal organs from damage
- Fat storage: as energy reserve
Functions of Skin
The most important functions of the skin include:
- Regulation of body temperature; the fat stored in the skin aids in insulating the body against heat and cold
- Protection of the body from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation and toxins
- Prevention of the loss of essential body fluids
- Acts as an excretory organ; it expels many toxic wastes along with sweat
- Helps in boosting the immunity
- Acts as a sensory organ
- Synthesis of useful substances such as vitamin D
Ten Most Common Skin Disorders
A skin disorder may arise in a particular layer of the skin and then move onto other layers, resulting in visible scars or far reaching metabolic effects. For ideal treatment and care, it is important to understand the underlying mechanisms behind the various skin disorders.
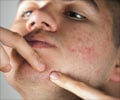
1. Acne: While acne is one of the most common skin disorders, it is also the most dreaded one, especially among the young who frequently carry it. Acne is caused due to any of the following:
- Increase in oil: Excessive production of the androgen hormone triggers oil overproduction that leads to acne flares
- Clogging of pores: Excess hormone levels result in the old skin cells becoming sticky and instead of being shed, they clog pores leading to acne
- Multiplication of the organism called Propionibacterium
- Inflammation of the skin

2. Shingles: Shingles (herpes zoster) is caused by the virus Varicella zoster, the same virus that causes chicken pox. The virus may remain dormant in the body of individuals following an attack of chicken pox, and at some later point of life, especially when the immunity of the individual weakens, this virus gets reactivated.
Symptoms:
- The appearance of painful blistering rash concentrated usually to one part of the body, commonly wrapping around the trunk or waist; it can also appear anywhere on the body. The pain is usually very severe.
- Fever.
- Headache.
- Fatigue.
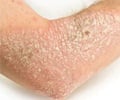
3. Eczema: Eczema is believed to be caused by a number of factors. Genes play an important role, along with environmental triggers and a severe immune reaction by the body.
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema and is found mostly in children. Adults experience allergic contact dermatitis when they come in contact with certain perfumes, cosmetic agents or even metal from jewelry. Nummular dermatitis is characterized by round coin-shaped (nummular) itchy and dry lesions.
Symptoms:
- Skin that is dry and scaly.
- Scaly skin is present as patches in feet, hands and folds of skin.
- On repeated scratching, these patches of skin may turn hard.
4. Skin cancer: It is one of the major diseases that affects the skin. Nearly, one million Americans are affected by skin cancer every year and one in 5 Americans are posed to get skin cancer during their lifetime. 1-2% of all diagnosed cancer in India is due to skin cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is more frequently detected than basal cell carcinoma.
There are different types of skin cancers depending upon the type of skin cells that are affected.
- Melanoma: Maximum death due to skin cancer is because of melanoma. It is formed in the melanocytes in the skin (cells that produce melanin). They are characterized by brown or black lesions present all over the body.
- Basal cell carcinoma: They develop in the basal cells and are characterized by raised pink bumps.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma: This rare type of skin cancer occurs in the endothelial cells, the cells that line blood vessels in the skin. They are characterized by brownish blue lesions in the hands and feet. The human herpes virus is believed to cause this skin cancer.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Red, scaly lesions are found in the areas of the body that are exposed to the sun. This form of cancer is most often seen among patients who have undergone an organ transplant.
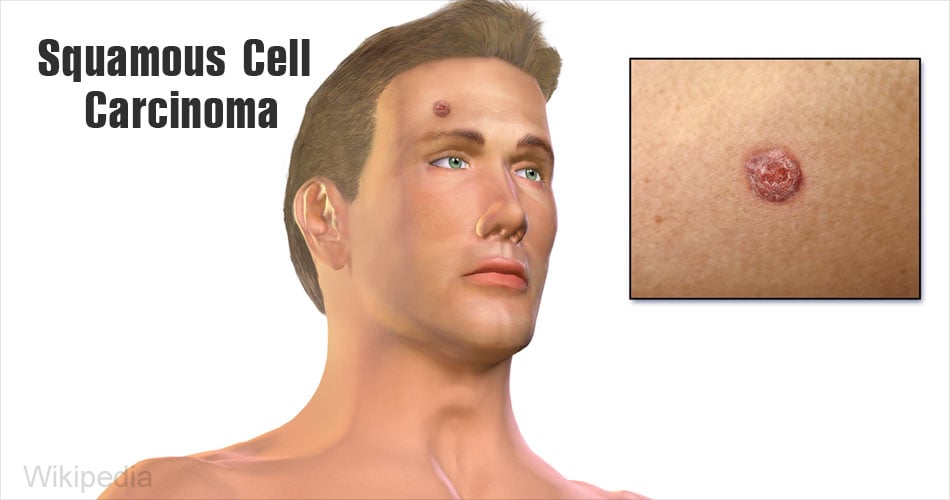
5. Psoriasis: This is an autoimmune disorder where the skin cells divide at abnormally rapidly rates. This leads to a buildup of cells on the surface of the skin, forming white patchy, flaky areas that are not shed.
Types:
- Plaque psoriasis: This type of psoriasis is also called psoriasis vulgaris. The skin is red and inflamed with silvery white patches of skin. These patches may burn or may be itchy.
- Guttate psoriasis: Guttate psoriasis commonly occurs in children due to a respiratory infection, injury to the skin, stress or due to certain drugs. In most instances, it resolves on its own within a few weeks.
- Inverse psoriasis: In this type of psoriasis, the patches do not have scales and are red and smooth. These patches are usually found in the armpits, buttocks and the folds of skin. This condition is worsened during excessive sweating.
- Pustular psoriasis: Pustular psoriasis is characterized by the presence of pus filled eruptions surrounded by red skin. It is precipitated by stress, sudden stoppage of certain drugs, intake of certain medication, pregnancy or exposure to certain chemicals.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: This is the most severe form of psoriasis and is characterized by reddish patches that can affect the heart rate, burning sensation or fever. Erythrodermic psoriasis should be treated immediately as it can lead to severe illnesses that include heart conditions and pneumonia.
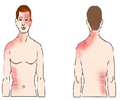
6. Rosacea: This skin condition is generally more popular among light skinned people. People who tend to blush or flush red in their face are commonly affected. Rosacea begins as redness around the nose and cheeks, and if left untreated, it can lead to pimples. Sometimes, excessive growth of cells can lead to an enlargement of the nose. Though there is no cure, treatment will help control the disease. There are four subtypes of rosacea based on the symptoms exhibited:

- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea: Visible blood vessels may be noticed along with excessive redness and flushing.
- Papulopustular rosacea: The red areas are accompanied by pimples and bumps.
- Phymatous rosacea: The nose gets bigger due to excess of skin and there is thickening of skin.
- Ocular rosacea: In this type of rosacea, there are manifestations in the eye like dry eyes, sty, swollen eye lids and in severe cases vision loss due to damage to the cornea.
7. Athlete’s Foot: Dermatophytes are fungi present in moist areas like shower cubicles, swimming pool lockers, moist shoes or wet socks and they lead to the development of itchy flaky skin. These could be present in the toes of the feet and in between the digits.
This infection of the skin can pass on from one infected individual to another when using wet shoes or when sharing shower cubicles. Sometimes, the infection may spread to a nail. Though treatable, it takes a long time to resolve. The fungi that cause this condition do not invade any deeper into the skin, but the cracks and openings caused by this fungus can lead to the entry of other bacteria (causing secondary infections).
8. Vitiligo: It is a condition in which the melanin producing cells either stop functioning or die. This can lead to patchy blotches of skin which are pale due to the loss of skin color.
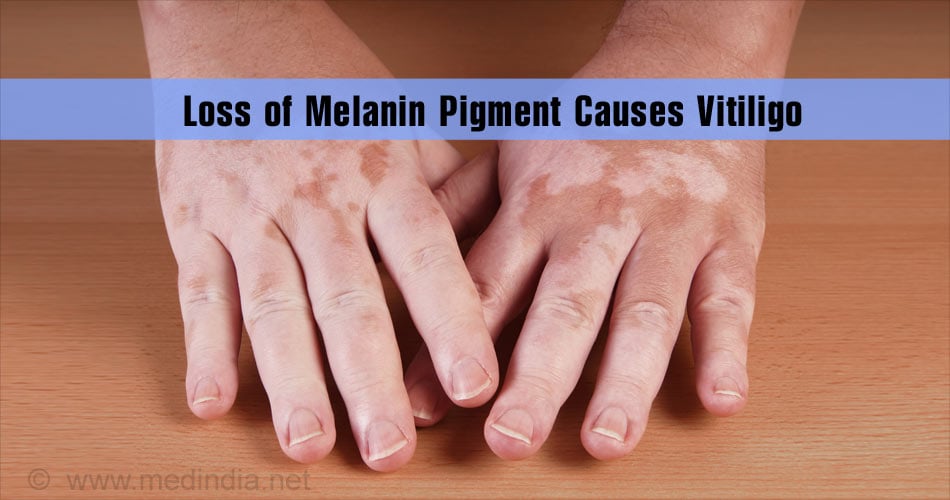
This disease condition is not contagious, infectious or fatal. However, patchy skin on the face, lips or even the eyes and hair can lead to embarrassment and psychological discomfort.
The disease is considered to be an autoimmune disease, where the body’s immune system attacks the melanocytes and leads to their loss. This could be due to specific mutations in the gene or due to the activity of certain chemical or even due to sunburn. There is no specific treatment for vitiligo and patients with small patches resort to skin grafting or tattooing to mask the patchy skin.
9. Hives: They are itchy, red patches of the skin that are caused due to an allergic reaction to food or certain substances. This condition, also called urticaria, affects nearly 20 percent of people at some point in their life.
Hair of pets (especially cats), blood transfusions (when not properly matched), certain antibiotics, insect bites, certain foods like shellfish or peanuts can lead to hives in susceptible persons.
Anti-histamines are part of the treatment regimen.
10. Age or Liver Spots: Black or brown spots on the exposed surfaces of the skin are called solar lentigines or liver spots. These age spots are caused due to exposure to sunrays, therefore, using sunscreen lotions and avoiding excessive exposure to the sun will aid in preventing the appearance of these spots. These spots are harmless but are often confused to be cancerous growths.
How are Skin Conditions Diagnosed?
A doctor would look at the physical presentation of the skin disorder to identify the skin condition that the patient suffers from. When allergy or certain bacterial, fungal or viral infections are suspected, there are skin tests available to determine the type of allergen or to identify the cause of infection.
- Scratch test: The skin in the forearm or back is cleaned with alcohol and specific areas marked with a pen. The suspected allergen is then placed on the skin, within the marked areas, after which a small scratch on the skin is carried out. This is to facilitate the entry of the allergen into the skin and is not meant to be a full prick that leads to bleeding. The scratch test is also called the prick test or the puncture test. The entire process of exposing the patient to the allergen takes between 5 to 10 minutes, after which the patient has to wait for 15 to 30 minutes to witness any visible reaction to the allergen.
- Intradermal test: This is similar to the scratch test, but the allergen is injected into the skin intradermally.

- Patch test: The allergen is added to a patch and this patch is then applied to the forearm or the back of the patient. To test for delayed response, the patient is usually asked to come back after 48 hours to observe for any reaction.
- Skin biopsy: A skin biopsy is performed to differentiate between a rash, malignant tumor or a benign growth. This procedure is used to remove skin samples that are used for further analysis under the microscope to determine the type of cells and the causative agent.
There are different types of skin biopsy procedures:
- Shave biopsy: A local anesthetic agent is applied to the site of biopsy and a scalpel (surgical blade) is used to remove a small section of the growth on the skin. Normally, the whole lesion or a part of it is removed. There is minimal bleeding which is arrested using medicine applied to the area. A shave biopsy is carried out when the lesion is suspected to be cancerous.
- Punch biopsy: This type of biopsy is performed when the lesions run deep. The whole lesion is removed and will require stitches. It is performed using a punch tool used for the skin.
- Incisional biopsy: A small piece of lesion is removed after the application of a local anesthetic agent. This is sent for further analysis and the treatment of the rest of the lesion is carried out after the result of the analysis.
- Excisional biopsy: This type of biopsy is performed when melanoma is suspected and is carried out by a surgeon. The entire lesion is removed and would require stitches (sutures) to close the wound. If a large part of the skin is removed, a skin graft is done to replace the skin that is removed.
What are the Treatment Options for Skin Disorders?
The treatment options depend upon the type of skin disorder.
- Excessive dryness of the skin would require the application of moisturizers to hydrate the skin.

- Allergic reactions lead to skin eruptions and antihistamines may be prescribed, depending upon the severity.
- Fungal infections would require the administration of anti-fungal agents.
- Cancerous growth would require chemotherapy and radiation therapy based on the stage of the disease.
Health tips
Here are a few health tips to prevent the contraction of skin diseases.
- Sun protection: Over-exposure to the sun and its UV rays results in excessive skin damage that can lead to sunburn or even skin cancer. Therefore, the number one tip would be to wear sunscreen or sunblock to prevent damage to the skin from sunrays. Staying away from direct sunlight from 11:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. would also provide protection.
- Wash hands well: Washing hands prevent the spread of infections, however, it is largely underrated.
- Include fruits and vegetables in the diet: Fruits and vegetables aid in providing the necessary nutrients to keep the skin glowing and to ward off certain skin conditions and diseases by fortifying the body.
- Attend to wounds: Skin is the biggest barrier against infections and a tear or a wound can open that barrier and increase the risk of infections. Moreover, untreated wounds may become severe and spread to other areas of the body.