Fish tapeworm
Definitive host: Humans, cats and bears.
Intermediate host: Water flea, small vertebrates, fish and other crustaceans.
Prevalence & Distribution: Eastern Europe, Uganda, Chile, North and South America, Scandinavia, western Russia, the Baltics, African countries and in some Asian countries where there is more consumption of freshwater fish.
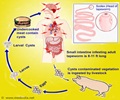
Mode of infection: Man who has the adult tapeworm excretes the eggs along with the feces. The eggs hatch out under optimum conditions into the ciliated larvae (coracidia). This is then ingested by the first intermediate host like the small crustacians. The crustaceans are then ingested by small freshwater fishes and the larvae develops into the sparganum which migrates into the tissue of the fish. When fishes, which harbor the larvae, are consumed by man in the raw state, the sparganum enter the human intestine and develops into an adult tapeworm. Sometimes the sparganum does not mature but moves about in the tissue and gets lodged in the sensitive areas of the eye or brain.
Symptoms: It competes with the host for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestines. Hence the patient becomes deficit in vitamin B12 and suffers from Pernecious anemia. Intestinal blockage by worms can cause gastrointestinal symptoms. Symptoms of pernicious anemia include easy fatigubility, numbness and tingling sensation in the limbs.