Cat Tapeworm
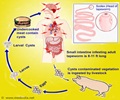
Tapeworm infection can affect cats or other mammals by typically settling in the small intestine. The tapeworm species that can cause infection in cats include Dipylidium Caninum, Taenia taeniaformis, Spirometra mansonoides, Dibothriocephalus latus or Echinococcus. Treatment to destroy tapeworms is a critical step in preventing transmission to humans especially children, and for averting damage to the cat's body. When treated promptly, prognosis is positive.
Definitive Host
Cats and rarely humans
Intermediate Host
Fleas are the intermediate host forDipylidium caninum. Lice are also an intermediate hosts for tapeworm but they are relatively uncommon parasites of cats. This means that the tapeworm is unable to complete its life cycle without the presence of fleas or lice in the environment. The cat must ingest an infected flea or louse in order to become infested.
The intermediate hosts of Taenia taeniaformis are mice, birds or rabbits.
Dibothriocephalus latus and Spirometra mansonoides are two uncommon tapeworms that can spread to cats via uncooked freshwater fish or a water snake.
Echinococcus tapeworms are rarely found in cats. Foxes, coyotes and wild rodents are important in the life cycle of this parasite.
Prevalence and Distribution
The most common internal parasite in adult cats is tapeworms.
The two common tapeworm species found in cats are Dipylidium caninum and Taenia taeniaformis.
Spirometra mansonoides is seen in outdoor cats along the Gulf Coast region, while Dibothriocephalus latus might be seen in the Gulf Coast region or around the Great Lakes.
Trappers and hunters in the north central United States and south central Canada may be at increased risk for infection with Echinococcus when strict hygiene is not practiced.
Mode of Infection
Human infection with cat tapeworms is rare yet possible. A person could acquire a tapeworm if they accidentally swallow an infected flea. Cat tapeworms do not present a health hazard to humans.
Human infection with Echinococcus is very rare and can cause serious, potentially fatal disease when humans become infected. Humans are at risk for infection when eggs of Echinococcus are passed in the feces of the dog and cat.
Rodent control and good hygiene are important in preventing the spread to humans.
Symptoms
Patients may not suffer from symptoms. Gastrointestinal symptoms may be present in some cases.