Evaluation for Palpitations
Clues to the diagnosis of arrhythmia and its type may be found in the information you give the physician. Keep a record of your episodes of palpitation. Try and find the cause of your palpitations. Examples are palpitations after drinking certain numbers of coffee or after eating some food or taking a new medication. Most commonly asked questions that need to be answered before starting on treatment are –
- What starts/precipitates your palpitations?
- How long do they last?
- Have you counted your heart rate and what was it?
- Could you tell if your pulse was regular?
- How do these episodes stop (abruptly on their own, with certain medications, with posture change or terminating exercise)?
- How often do you feel irregular heartbeat?
- Have you felt short of breath, light headed, chest pain or fainted during an episode of palpitation?
The answers may help doctors determine how serious your palpitations are and what is the underlying cause for this symptom?
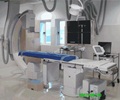
Electrocardiogram [ECG/EKG] records the electrical activity of your heart. The test usually takes less than 15 minutes to perform. Electrical leads will be placed on your chest, hands and feet, which will be connected in turn to a monitor. Any abnormality in the heart rhythm can be seen on the monitor, documented and printed on the paper.
In patients where the palpitations comes and goes, the arrhythmia may not be documented during a doctor’s visit. They may be sent home with a monitor attached to their chest. A Holter monitor can be worn for 24 or 48 hours. There is a recording device inside the monitor to constantly record the ECG. Once the monitor is returned to the medical facility, the data are transferred to a computer and analyzed. In some patients, the palpitations occur few times a month. Another monitor called the Event monitor or a Loop recorder can be used to capture these abnormal rhythms. When the symptom occurs, you record the ECG by pushing a record button on the monitor attached to you. About five minutes’ data can be documented in this machine and can be transferred to your doctor through a landline or mobile telephone.
On auscultation, the doctor can hear the abnormal heartbeat or a murmur if there was any valve damage causing the palpitations.
Blood tests are done to rule out hyperthyroidism and hypoglycemia. Potassium and magnesium levels can be measured. They can alter the heart rhythm when abnormal. If you are on medication digoxin, it is advisable to check the level of digoxin in blood.
Echocardiogram is performed to check the heart structures and function. It can help diagnose valve disease and coronary artery disease.
A Treadmill exercise test helps reveal any exercise-induced arrhythmias.
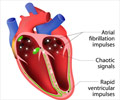
Electrophysiology study [EPS] is advised to patients when certain types of arrhythmias are identified, that can lead to sudden cardiac death or severe complications. It is an invasive procedure similar to cardiac catheterization. Wires are inserted through the groin or the neck to the heart using catheters and guide wires. When the wires are in place, electrical activity in different areas of the heart is recorded. Heart muscles can also be induced to reproduce the abnormal rhythm. Specific areas of the heart muscles that are causing the abnormal electrical impulses can be located and treatment to the area be given.