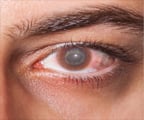
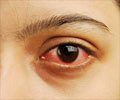
Causes and Symptoms of Eye Infections
Bacteria, viruses and fungi are the common causative agents of eye infections.
Microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses and fungi attack either the surface of the eye or enter the eye, thereby causing eye infection.
Various types of eye infections include:
- Conjunctivitis: Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory condition of the conjunctiva, the transparent membrane that lines the anterior part of the white of the eye and inner surface of the eyelids. It is commonly referred to as ‘pink eye’. Besides infection, conjunctivitis can also be caused by trauma, exposure to toxic substances or autoimmune disease. Infective conjunctivitis may be bacterial or viral, acute or chronic in nature. Fungal conjunctivitis is very rare.
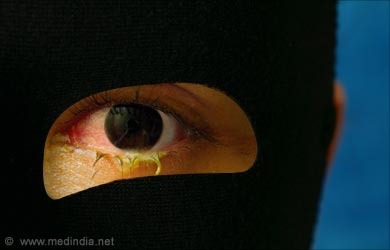
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses like adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, enterovirus, Epstein Barr virus and varicella zoster virus. It is highly contagious and usually resolves in 2 weeks. Symptoms include:
- Red and itchy eyes with scanty watery or clear discharge
- Eye swelling and a foreign body sensation may be present
- The patient may also suffer from fever or upper respiratory tract infection at the same time
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria like staphylococcus, streptococci, Neisseria gonorrohoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis.
Symptoms of Eye Infections
- The patient has a thick purulent discharge with less itching as compared to viral conjunctivitis. The eyelids tend to stick together in the morning due to crusting. This feature is referred to as ‘glue eye’
- Mild to moderate stinging sensation, redness of eye and a foreign body sensation may be present.
- Gonococci, which cause the sexually transmitted disease gonorrhea, may cause conjunctivitis in neonates or young, sexually active patients. The discharge is usually thick and green in color. Eye swelling is usually present. The patient may also suffer from an infection of the genitourinary tract at the same time.
- Infection with Chlamydia trachomatis, another bacteria responsible for sexually transmitted disease, results in conjunctivitis with red eye and excessive mucopurulent discharge.
- Keratitis: Keratitis refers to inflammation of cornea, the transparent dome that covers the front central part of the eye. Besides, bacterial, viral and rarely fungal infection, keratitis may be caused by exposure to ultraviolet rays, certain chemicals and the use of contact lenses. Keratitis is a serious condition, which if left untreated, can result in loss of vision.
- Viral keratitis is often caused by herpes simplex, varicella zoster and Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus (CMV).
- Bacterial keratitis is commonly caused by staphylococci and pseudomonas species, Moraxella catarrhalis in immunocompromised patients, and N.gonorrheae and C. trachomatis in sexually active patients.
- Fungal keratitis is very rare and may be caused by yeast or filamentous fungi.
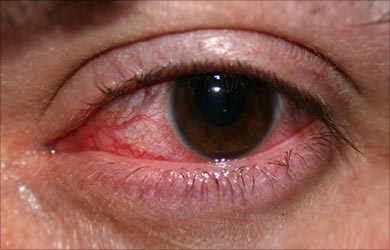
- Contact lens users often suffer from keratitis due to acanthamoeba.
- Keratitis results in an acutely red, painful eye with a foreign body sensation, light sensitivity, excessive tears and vision changes.
- Examination of the eye may reveal an ulcer or abrasion, and swelling of the cornea.
- Uveitis: Uveitis refers to inflammatory of the uvea of the eye, which is the middle pigmented layer.
- Besides infection, it is also caused by autoimmune disorders, injury or cancer.
- Symptoms include severe redness of the eyes with headache, pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity and dark floating spots in the field of vision.
- Endophthalmitis: Endophthalmitis refers to inflammation of intraocular cavities. The infection may be caused due to direct introduction of bacteria in the eye due to trauma or surgery, or due to bacteria entering into the eye via the blood in conditions like endocarditis.
- Periorbital and Orbital cellulitis: Infection of the orbit of the eye and the soft tissues surrounding it result in cellulitis. It is commonly caused by bacteria like
Staphylococcus aureus , Streptococcus pyogenes or Streptococcus pneumonia. It may follow a sinus infection or an insect bite. - Symptoms include upper or lower lid swelling, pain and tenderness of periorbital tissues.
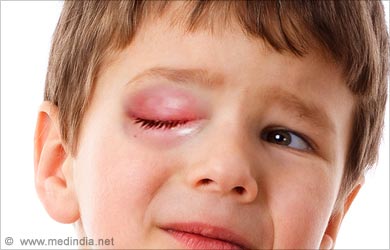
- Hordeolum: Hordeolum (i.e. Stye) is an infection of the hair follicles of the eyelashes and the adjacent meibomian glands. It is a bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus species.
- Symptoms include a localized swelling around the eyelash with the formation of a small abscess and pain.
- Dacrocystitis: Dacrocystitis is an acute infection of lacrimal sac, through which tears come out of the eye. It is a bacterial infection, commonly caused by Staphylococcal species.
- Symptoms include pain, swelling and redness at the inner angle of the eye.
Risk Factors of Eye Infections
People at risk of developing eye infections include:
- Those with decreased immunity like newborns, elderly, diabetics and other immunocompromised individuals.
- Contact lens users

- People with dry eyes
- People with autoimmune diseases or infections in other parts of the body
- People who suffer from trauma to the eye or have undergone eye surgery
- Those who maintain poor hygiene
- Use of old eye cosmetics and contaminated eye makeup brushes.