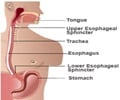
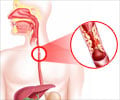
Causes of Barrett’s Esophagus
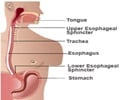
Normally, the esophagus is protected from the acid in the stomach by a valve at the lower end. Sometimes, this valve may not close efficiently. Thus, acid from the stomach regurgitates into the esophagus. This condition is called
Risk Factor -
Conditions that increase a person’s risk for developing Barrett’s esophagus include -
- Age – Barrett’s esophagus usually affects people between 55 and 65 years of age.
- Obesity- An increase in waist size predisposes a person to Barrett’s esophagus.
- Male sex – Barrett’s esophagus is seen more commonly in males than in females.
- Treatment of H pylori infection – H pylori is a bacterium found in the stomach that causes stomach ulcers. It appears to reduce the incidence of Barrett’s esophagus. Hence, treatment of H pylori infection may result in an increase in the number of Barrett’s esophagus cases.
- Smoking and alcohol cause increase in acid reflux into the esophagus and can contribute to Barrett’s esophagus
- Fat, chocolate, peppermint and caffeine reduce the lower esophageal sphincter tone and can cause reflux.