- Parasites - Balantidiasis (also known as Balantidium coli Infection) - (http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/balantidium/)
- Neafie RC, Andersen EM, Klassen-Fischer MK. Balantidiasis.
- Schuster FL, Ramirez-Avila L. Current World Status of Balantidium coli. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2008;21(4):626-638. doi:10.1128/CMR.00021-08.
- Clinical Presentation of Balantidiasis - (http://web.stanford.edu/group/parasites/parasites2003/balantidium/clinical_presentation.htm)
- Dhawan S, Jain D, Mehta VS. Balantidium coli: an unrecognized cause of vertebral osteomyelitis and myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(3):310-313.
- Sharma S, Harding G. Necrotizing lung infection caused by the protozoan Balantidium coli. The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2003;14(3):163-166.
- Karuna T, Khadanga S. A rare case of urinary balantidiasis in an elderly renal failure patient. Tropical Parasitology. 2014;4(1):47-49. doi:10.4103/2229-5070.129165.
- Diagnosis of Balantidiasis - (http://web.stanford.edu/group/parasites/parasites2003/balantidium/diagnosis.htm)
- About Balantidiasis - (https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/balantidiasis/)
- PomajbÃková K et al. Novel Insights into the Genetic Diversity of Balantidium and Balantidium-like Cyst-forming Ciliates. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(3):e2140. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002140
What is Balantidiasis?
Balantidiasis is a rare bacterial intestinal infection in humans caused by an intestinal parasite called Balantidium coli. The bacterial infection has the potential of being a zoonotic disease in humans as pigs serve as hosts for the parasite. However, the parasite is present in other animals like rats, chimpanzees, gorillas, fowl, orangutans, cockroaches, and turtles. In 1857, Malmsten detected the parasite in two individuals who had severe diarrhea. The parasite tends to live in the colon and cecum of humans.
Balantidiasis is a rare disease that is seen all over the world. It is detected more frequently in tropical regions and warm temperate regions, especially in areas where pigs are present. However, the infection has been observed in Russia and the Scandinavian countries like Sweden, Finland, and Norway. This disease is a case of poor hygiene practice that can result in contagious infection in humans.
What are the Causes of Balantidiasis?
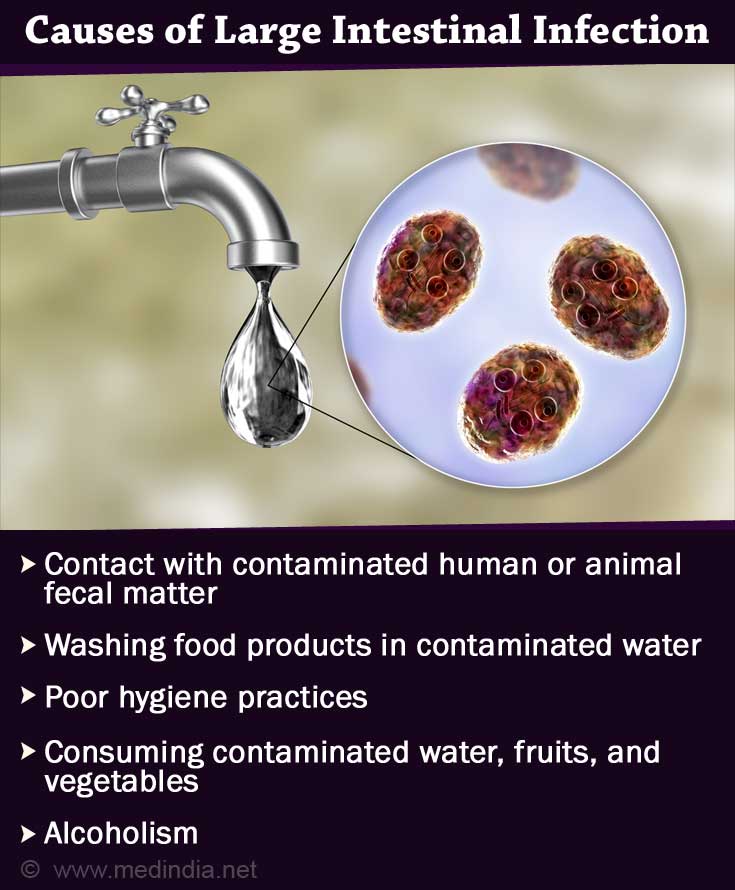
Balantidiasis is caused by a large intestinal parasite, Balantidium coli. The infection is caused by contact with contaminated human or animal fecal matter. In humans, if food products are washed with contaminated water, it becomes a source of infection. Poor hygiene practices are a source of contamination. The infection can also occur by consuming contaminated water, fruits, and vegetables which have been in contact with infected individuals.
Other factors that can predispose an individual to Balantidium coli infection are:
- Alcoholism
- Number of infecting parasites
- The status of the normal bacterial content in the intestine
- Immunity acquired by living in communities which are regularly exposed to the Balantidium bacteria
- Presence of other health conditions like cancer (abdominal lymphoma)
- Nutritional intake
- Organ transplants
- Living in institutions like orphanages, senior citizen homes, prisons, and asylums
- Farmers and zookeepers who are in contact with infected animals
- Infected sludge that is obtained from sewage treatment and is used as fertilizer
- Infected pigs, rats, monkeys, and cockroaches
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Balantidiasis?
There are 3 ways in which humans show signs of Balantidiasis:
- Some individuals may not experience any symptoms following infection.
- Certain individuals experience severe symptoms like blood and mucus in the stools. Individuals have frequent stools that may number more than 20 in a day.
- Following infection, individuals may experience abdominal pain, cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea without blood.

Other symptoms include insomnia, weight loss, headache, and muscle weakness.
Balantidium coli also cause infections in the bone, lungs, and genitourinary tract.
There are certain health conditions which have similar symptoms as Balantidiasis. These health conditions are irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, chronic erosive gastritis, amoebic dysentery, Crohn’s disease, shigella dysentery, chronic fungal bowel infections, amebiasis, intestinal tuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Hence, doctors need to take this into account before confirming a Balantidium coli infection.
How to Diagnose Balantidiasis?
Balantidiasis is diagnosed with slide samples of secretions of the intestine or stool samples. It is the easiest form of diagnosis as the parasites are large in size and actively motile. Cysts can also be detected with staining. Balantidium cysts are larger and aid in detecting the exact cause of dysentery. However, intense staining may obscure the cysts or may result in certain structures within the stools to resemble the cysts. This may lead to misdiagnosis. In order to confirm the diagnosis, stools should be checked frequently as the cysts are excreted at regular intervals.
Additionally, the colon wall can be analyzed by sigmoidoscopy to detect damage to the wall by parasitic infection. A long sigmoidoscope is used to examine the tissue and also extract a small section of the tissue for analysis (biopsy).
Infection of the lungs can be detected with phase contrast microscopy. This reveals the typical features of Balantidium coli and avoids confusion with other infectious organisms.

Flotation and sedimentation are used to concentrate Balantidium coli in the samples of stools to favor diagnosis.
How to Treat Balantidiasis?
The main drugs used to treat Balantidiasis are iodoquinol, metronidazole, and tetracycline. Metronidazole is administered for 5 days, tetracycline dosage is for 10 days whereas iodoquinol is administered for 20 days. The other drugs that may be used are doxycycline, ampicillin, nitrimidazine, paromomycin, and carbasone.

Health Tips
The best way to prevent this condition is to practice good hygiene. Avoid eating food and drinking water that have been contaminated or have been in contact with a contaminated person. Pigs should not be allowed to use water resources that are connected to drinking water reservoirs. Pigs should also be prevented from coming in contact with crop fields.