Glossary
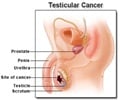
Cancer: A term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body.Carcinogen: Chemical or substance that can cause cancer.
Carcinoma: Cancer that begins in tissues lining or covering the surfaces (epithelial tissues) of organs, glands, or other body structures. Most cancers are carcinomas.
Pap Smear Test: Screening test for cervical cancer which detects cancers early and spots precancerous conditions. Also called the Pap Test this procedure involves a few cells being scrapped off the cervix, put on a microscope slide, dyed and examined.
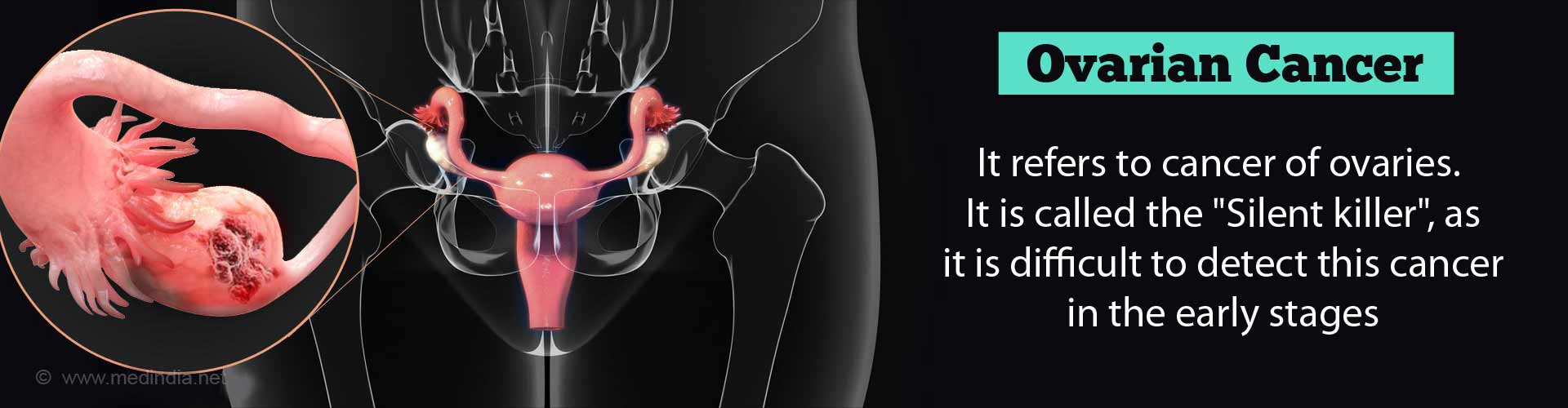
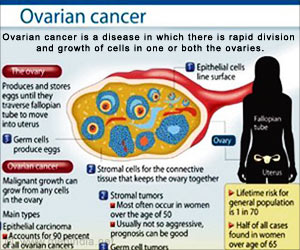
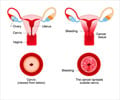
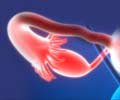
Ovary: The female reproductive organ that is located on each side of the uterus and produces ova, or eggs.
Transvaginal ultrasound: A type of pelvic ultrasound adopted for internal examination of the female reproductive organs through the vagina
Gynecologist: A gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in and treats ailments related to female reproductive health.
Ascites: Collection of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
BMI: Also known as Body Mass Index. It is a measure used to determine an adult person’s weight in relation to his height.
Colonoscopy: A minimal invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a thin lighted tube through the anus. A high resolution camera at the tip of the tube helps to visualize the insides of the large bowel. Small instruments can be passed through the tube and tumors can be either removed fully or biopsy samples can be taken.
Endometriosis: A condition where the endometrium, which is the inner lining of uterus and normally, confined to the uterus is present outside the uterus. Endometriotic tissue is usually seen over the ovaries, fallopian tubes, rectum and other pelvic organs. It can lead to pain in lower abdomen and infertility.
In-vitro fertilization: Known as IVF. During this procedure, eggs are collected from the female and fused with the sperm of the male in the laboratory. The resulting embryo is then implanted in the female’s uterus.
Intravenous drugs: Medications that are injected directly into the veins.
Laparoscopy: A minimal invasive surgery that makes use of a thin lighted tube to look inside the abdomen. A small cut is made in the umbilicus and the lighted tube is inserted inside the abdominal cavity. The tube has a high resolution camera at the tip of the tube. With the help of the camera, the inner parts of the abdomen are visualized on a monitor. With the help of 2-3 lower abdominal incisions, small instruments can be passed and the tumors/cysts can be removed or can be biopsied.
Omentum: A layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the abdominal organs.
Ultrasound guided percutaneous biopsy procedure: Under ultrasound guidance, a needle is passed through the skin into the ovarian tumor and a piece of the tumor is taken for tissue biopsy.