- Triple X syndrome - (https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/triple-x-syndrome)
- What is triple X syndrome? - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/triple-x-syndrome/symptoms-causes/dxc-20164623)
- Trisomy X - (https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/trisomy-x/)
What is Triple X syndrome?
Triple X syndrome is a genetic disorder seen in females characterized by the presence of an extra X chromosome.
Triple X syndrome is also referred as:
- 47, XXX
- 47, XXX Karyotype
- 47, XXX Syndrome
- XXX Syndrome
- Trisomy X
Facts on Triple X syndrome
- It is seen only in females
- It is not an inherited disorder
- The syndrome is seen in 1 among 1000 newborn girls
- Some cases go undiagnosed because of the absence of symptoms
- Approximately 10 percent of cases are diagnosed
Genetics of Triple X syndrome
Normally each individual has 46 chromosomes of which two are sex chromosomes namely X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome.
Females born with triple X syndrome have 3 X chromosomes, so the total chromosome number is 47 because of an additional X chromosome.
Some females with triple X syndrome have the extra X chromosome only in some cells, which is called as 46, XX/ 47, XXX mosaicism.
What are the Causes And Risk Factors of Triple X syndrome?
Triple X syndrome is usually not inherited. It occurs when the reproductive cell i.e., the egg or sperm has two X chromosomes due to nondisjunction of chromosomes during their formation. When one such cell (egg/sperm) is involved in the formation of the zygote, it leads to the triple X syndrome.
The cause of 46, XX/ 47, XXX mosaic form is due to an abnormal cell division during the early embryonic stage which leads to an extra X chromosome in only some cells. It is also not hereditary.
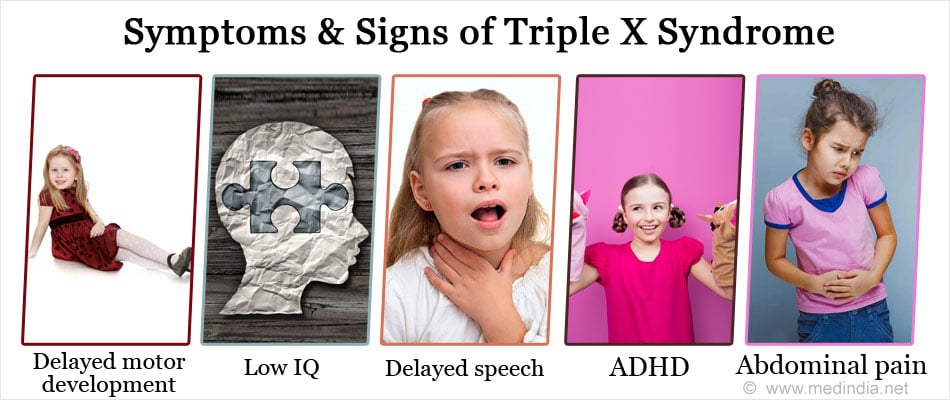
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Triple X syndrome?
The symptoms and signs of the triple X syndrome vary widely among the patients. The affected female patients may be asymptomatic or may have a few symptoms or many abnormalities. The following are the abnormalities that may be seen in females with triple X syndrome.
- The height is more than the average female height with long legs. They have a height above or equal to 75th percentile
- Delayed motor development like walking and sitting
- Weak muscle tone (hypotonia)
- Low IQ: 10-15 points lower than the siblings
- Delayed speech and language skills
- Behavioral and emotional problems
- Deficit in memory, judgment and information processing
- Little finger bends or curves abnormally called clinodactyly
- Infants with triple X may have epicanthal folds (it is a part of the upper lid which forms a fold and covers the inner eye corner), hypertelorism (an increase in the space between two eyes) and small head circumference
- Anxiety
- Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD): Children with ADHD exhibit excessive activity, lack of attention and uncontrollable behavior
- Abnormal ovarian development (ovarian dysgenesis)
- Early or delayed puberty
- Premature ovarian failure, Infertility
- Renal agenesis (failure to develop) renal dysplasia ( abnormal development)
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Seizures
- Flat feet
- Constipation, Abdominal pain
- Pectus excavatum ( abnormal chest wall which is concave or sunken in)
- Heart abnormalities
How do you Diagnose Triple X syndrome?
Triple X syndrome is suspected when the patient presents with any of the symptoms or delayed puberty or other menstrual abnormalities.
Chromosomal Analysis: Analysis of the chromosomes in the blood cells of the affected individual can confirm the diagnosis in suspected cases.

Other diagnostic methods include Prenatal diagnosis which may be done in certain patients for other reasons and the condition diagnosed incidentally.
Chorionic villous sampling: Chorionic villous sampling (CVS) is performed in the pregnant females to check for the chromosomal abnormalities in the growing fetus. The chorionic villi are present in the placenta. A bit of placental tissue is collected and the cells in the tissue are processed to check the chromosomes. If the fetus has triple X syndrome the cells will have an extra X chromosome.
How do you Treat Triple X syndrome?
Treatment for the triple X syndrome depends on the age at disease presentation, the severity of the disease and the symptoms at presentation.
Children:
If a newborn is diagnosed with triple X syndrome the child should be assessed for the following:
- Before 4 months of age: Developmental assessment to evaluate the muscle tone and strength
- Before 12 months of age: Language and speech assessment
- At preschool age: Pre-reading assessment to evaluate any early signs of the reading problems.
- In children with triple X syndrome, the assessment of kidney and heart function is necessary.
In children with triple X syndrome, early assessment and intervention show a great response. Speech therapy, developmental therapy, physical therapy, occupation therapy and counseling are the key intervention measures when needed.
Treatment for anxiety and ADHD is essential when found in the children.
Young Girls:
For the girls with triple X syndrome, adolescence may be a challenging phase of life and they may require a short period of counseling.
Women:
In women with infertility and menstrual disturbances, careful assessment to check for the presence of the primary ovarian failure is required.
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling among the affected members and their families is beneficial.
How do you Prevent Triple X syndrome?
Triple X syndrome is not a preventable condition.










