- Telemedicine E Health - (https://www.isfteh.org/)
- Telemedicine - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/telemedicine)
- Breen G, Matusitz J. An Evolutionary Examination of Telemedicine: A Health and Computer-Mediated Communication Perspective. Soc Work Public Health. 2010 Jan; 25(1): 59–71. doi: 10.1080/19371910902911206
- Hjelm NM. Benefits and drawbacks of telemedicine. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 2005; 11: 60–70
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine, which literally translates to ‘healing at a distance’, involves the use of modern information and communication technology to make health care and health information accessible to people from a distance.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined telemedicine as follows - “The delivery of health care services, where distance is a critical factor, by all health care professionals using information and communication technologies for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of health care providers, all in the interests of advancing the health of individuals and their communities.”

The following features characterize telemedicine:
- Provides clinical support
- Involves using information and communication technology for the purpose
- Connects persons who are not in the same place, thus overcoming geographical barriers to provide health care.
- Aims to improve the health outcome for the patient
Telemedicine versus Telehealth
The terms telemedicine and telehealth are often used interchangeably. Broadly, telemedicine refers to provision of mainly clinical services from a distance, while telehealth also provides non-clinical health-related services such as administrative meetings, continuing medical education and training programs in addition to clinical services.
Brief History of Evolution of Telemedicine
Among the earliest recorded accounts of telemedicine is the use of telemedicine in the early part of the 20th century to transmit electrocardiographic (ECG) data through telephone wires. Modern telemedicine derived its impetus from the advancements in the field of information and telecommunication technology, especially the internet boom in the 1960’s.
The early forms of telephonic and radio communication in telemedicine have largely been supplanted by video telephony and telemedical gadgets that enable in-home health care access.
What are the Different Types of Telemedicine?
Broadly telemedicine can be classified into three major types, namely:
- Store and forward
- Remote patient monitoring
- Interactive or real time services
Store and forward
In this type of telemedicine, there is no physician-patient interaction or the presence of both the parties concurrently. The patient information in the form of medical images or bio signals are transmitted via electronic media to the physician, who reviews it at a convenient time and provides expert opinion. A precise and well-structured history and clinical background of the patient, preferably in electronic form is included along with the images for the benefit of the physician.
The ‘store and forward’ type of telemedicine is useful in the medical diagnostic fields of pathology and radiology, and dermatology. The major drawback of this form of telemedicine is that the physician cannot obtain the medical history directly from the patient or perform a physical examination, but instead has to rely on the information provided in electronic form.
Remote patient monitoring
This type of telemedicine involves monitoring the patient remotely using various technological devices. It is especially useful in the follow-up of chronic conditions such as diabetes, asthma, and heart disease. The outcomes appear to be comparable to traditional physician-patient encounters. It might be cost-effective and saves patients the trouble of traveling long distances with their health condition for frequent follow-ups.
Other applications of remote patient monitoring include management of joint disease and home-based nocturnal dialysis, to name a few.
Interactive and real time services
In this type of telemedicine, there is an interaction between the physician and the patient, for example, over videoconferencing, with the need for both to be present simultaneously. It is possible to obtain a history and perform several assessments in this form of telelmedicine.

Global Statistics and Facts on Telemedicine Services
Statistics according to the WHO region related to the four fields of telemedicine - teleradiology, telepathology, telepsychiatry and teledermatology are mentioned below:
- Regions of Southeast Asia, Europe and Americas had the highest proportion of established telemedicine services.
- Southeast Asia and Europe had high level of established teleradiology programs compared to the global rate.
- African and Eastern Mediterranean had the lowest proportion of established telemedicine services.
Additional facts on telemedicine are mentioned below:
- High income countries have a higher proportion of established telemedicine programs, probably due to presence of well-developed information and communication technology systems, and allocation of funds for health care.
- Store and forward initiatives are generally implemented with lesser difficulty, compared to real time services, since they require less bandwidth for data transfer compared to real time services requiring higher bandwidth for videoconferencing purposes.
- Telepathology, teleradiology and teledermatology services are less bandwidth intensive and more often employed than telepsychiatry, which requires a real time doctor-patient interaction.
- Globally, 25 percent of countries reported having a national telemedicine policy or strategy.
- The global revenue from the telemedicine market is expected to reach around 4.5 billion U.S. dollars by 2018.
- In a survey conducted in the US, more than 70 percent of respondents aged 18 to 44 were open to the idea of telemedical services.
- In the UK, 10.2 percent of healthcare professionals employed health information collected via smartphones as of January 2015.
- More than half of the hospitals in the US have an established telemedicine program.
- Insurance companies in the US are required to pay for telemedicine services with certain limitations in at least 29 states.
What are the Specialties in which Telemedicine can be Employed?
Telemedicine is used in the following specialties:
1. Telenursing involves the use of information and communication technology to provide nursing care and services to patients even in the presence of physical distance.
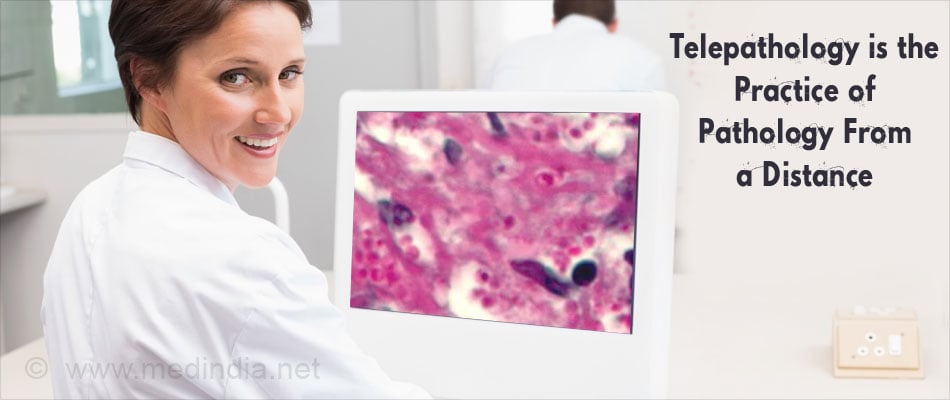
2. Telepathology is another area where the transmission of high quality microscopic images through the internet can be used for teaching, diagnostic and research purposes. It is necessary for a qualified pathologist to choose the appropriate, representative high quality image to be sent for analysis.
3. Teleradiology – As discussed earlier, radiology is one of the areas where telemedicine is employed in a big way. Radiological images such as x-rays, CT scans and MRI are transmitted via the internet to a radiologist or physician, who needs to have a computer with a high quality screen display, and if possible, a printer that prints high quality images.
4. Telepharmacy - In telepharmacy, pharmaceutical care is made accessible to patients at locations where they may not have access to a pharmacist. The pharmacist can monitor treatment, counsel patients about intake of medications, and authorize prescription drug refills using
Remote dispensing of drugs using automated packaging and labeling systems is also an example of telepharmacy. These services can be provided at retail pharmacies or at hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and other health care outlets.
Telepharmacy may also be used for education, training and providing management services to pharmacists at remote locations.
5. Teleophthalmology - Using digitized medical equipment and communication technology, optimal eye care facilities and monitoring of chronic eye conditions such as

6. Telecardiology – Specialist care and opinion in fields such as cardiology may be made accessible to patients by transmitting their ECG’s and other test results using the internet to experts at the receiving end.
Before the advent of internet, the then available technology employed wireless transmission of ECG images from the patient’s home or the ambulance to a central location in the hospital for cardiologist review. Interestingly, telemedicine was used way back in 1906 by Einthoven, the inventor of the ECG, to transmit electrocardiographic data from the hospital to his lab via telephone wires.
Telecardiology can also be used to monitor the heart rhythm of patients implanted with pacemakers living in remote locations. In developing nations, electronic stethoscopes may be used as recording devices to transmit heart sound of the patient.
7. Teledentistry involves the use of electronic media for the purposes of dental care, and consultation and creation of public awareness regarding dental health.
8. Telepsychiatry – Videoconferencing and other communication technologies can be used to make accessible specialist psychiatry services to persons living in underserved locations.
Diagnosis, follow up and monitoring of drug intake of such patients is possible. Such facilities also permit consultation between psychiatrists and for the provision of educational programs.
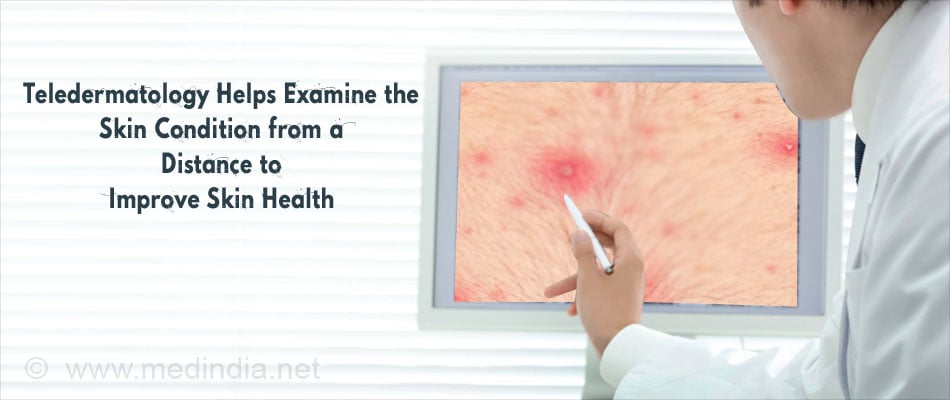
9. Teledermatology - involves the use of audiovisual data transmission of skin conditions for specialist consultation, diagnosis and treatment. Teledermatology can also be used for educational purposes. In this way, patients living in places where specialist care is inaccessible can be served.
10. Telerehabilitation refers to the use of communication technology to provide rehabilitation services to patients that include speech therapy, occupational therapy, neuropsychology, physical therapy and audiology.
Telerehabilitation enables health care to be delivered to patients unable to travel to the clinic or hospital due to their disability, and for expert consultation at a distance.
11. Teletrauma care uses modern communication tools to provide expert health care to patients in a trauma or disaster situation. Doctors and health personnel at the scene of disaster or trauma can interact with specialists via the internet or smartphones to help in assessing the severity of injuries and to determine management, and whether a particular patient might have to be shifted to a secondary or tertiary care center for further management.
Telemedicine is also being employed in the intensive care unit (ICU) setting to minimize the spread of infection. A specialist with his team of doctors, nurses and residents can watch live video stream of vital signs and other data from the patient’s bedside, sitting in a conference room. They can offer inputs on management and patient care to the clinicians at the bedside.
Some trauma centers use telemedicine to deliver trauma education and management lectures to doctors and health personnel at remote locations via videoconferencing. Operative procedures may also be beamed live to residents in distant locations for educational and training purposes.
What are the Benefits of Telemedicine?
Telemedicine offers the following benefits namely:
- Availability of healthcare to patients living in rural or underserved areas without necessity to travel to the hospital.
- Useful in post-disaster, natural calamity situations or other emergency situations when traveling is not possible.
- Elderly patients and persons with chronic illnesses can have regular follow-up and monitoring through telemedicine.
- Monitoring of drugs and dose management can be done through telephone.
- The time for travel is saved and the cost of treatment may also come down.
- Facilitates health education by allowing students or health workers to observe and listen to experts in their respective fields. Medical teaching is possible by making available academic material and case presentations through webcasts, and teleconferencing.
- Electronic search engines, online medical sites and journals provide latest research news helping health professionals to stay updated. Specialists can also communicate with each other to solve difficult cases.
- Allows patients to participate in the decision making process since knowledge is made available to them.
- Presence of computerized database, especially in primary care settings allows the physician to access patient records and for multidisciplinary collaboration whenever needed. This could improve the quality of patient treatment.
- Home-based dialysis options are available to patients through video link supervision, whenever needed.

- Can possibly overcome the risk of transmission of infection between health care professional and the patient, or between patients.
What are the Potential Barriers of Telemedicine?
The following may be considered as possible downsides of telemedicine:
- Lack of direct interaction between the physician and the patient
- High cost of communication and data management equipment and its maintenance, which may not be easy for older people living alone
- Necessity to train personnel technically to handle communication and data management equipment
- Possibility of error when health care is delivered in the absence of a trained health professional
- Possibility of misuse of patient data through electronic transmission
- In certain instances, time taken to provide health care through telemedicine may actually be longer than traditional consultations because of increased time taken to assess and treat patients through virtual interactions
- Poor quality of records or images made available to the physician at the receiving end and omission of relevant clinical information might affect the quality of health care delivered
- Absence of proper legal regulations for some of the telemedicine practices
- Difficulty in claiming insurance or reimbursements in certain fields
What is the Future of Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is being increasingly adopted in many centers across the globe, and gradually becoming an acceptable form of health care delivery. Telemedicine can offer a suitable alternative to traditional curative as well as preventive care, and could result in better health outcomes for the patient. In the developed world, it is possible that telemedicine might one day shift healthcare delivery into the confines of the patient’s home from the hospital.
Extensive research and studies have been conducted on the use of telemonitoring of remote patients, with most of them showing how valuable remote healthcare could be.
Results have shown a decreased need for hospital readmissions, reduced home nursing visits and lower overall health costs. Additionally, patients and their caregivers using telemedicine technology have reported higher satisfaction with quality of treatment provided. These findings have in fact encouraged many countries – such as the United Kingdom – to integrate remote healthcare into their present healthcare systems.
If anything, the one question that begs answering is ‘when will telemedicine become an integral part of standard health care?’






