- Penack O, Becker C, Buchheidt D, et al. Management of sepsis in neutropenic patients: 2014 updated guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (AGIHO). Ann Hematol. 2014;93(7):1083-95.
- Kruse JM et al., “Neutropenic Sepsis in the ICU: Outcome Predictors in a Two-Phase Model and Microbiology Findings,” Critical Care Res and Pract. 2016;2016, Article ID 8137850, 9 pages. - (https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8137850)
- Clarke RT et al. Neutropenic sepsis: management and complications. Clin Med. 2013;13(2):185-187. - (https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8137850)
- Prevention and Management of Neutropenic Sepsis in Cancer Patients. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK373673/)
- Bate J et al. Neutropenic sepsis: prevention and management of neutropenic sepsis in cancer patients (NICE Clinical GuidelineCG151). Arch Dis in Childhood – Ed and Pract. 2013;98:73-75. - (https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8137850)
- Neutropenic sepsis: prevention and management in people with cancer - (https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg151/chapter/Introduction)
- National Collaborating Centre for Cancer. Neutropenic sepsis: prevention and management of neutropenic sepsis in cancer patients. 2012. - (https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg151/evidence/evidence-review-pdf-188303582)
- O. Penack, D. Buchheidt, M. Christopeit, M. von Lilienfeld-Toal, G. Massenkeil, M. Hentrich, H. Salwender, H.-H. Wolf, H. Ostermann; Management of sepsis in neutropenic patients: guidelines from the infectious diseases working party of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology, Annals of Oncol. 2011;Vol 22(5):1019–1029. - (https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8137850)
- Mapes D. Hutch news: After chemotherapy, immune system recovery may be slower than believed. Updated Jan 26, 2016. Accessed Mar 18, 2019. - (https://www.fredhutch.org/en/news/center-news/2016/01/chemotherapy-immune-system.html)
- Ramzi J et al. Predictive factors of septic shock and mortality in neutropenic patients. Hematology. 2007;12(6):543-548. - (https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8137850)
What is Neutropenic Sepsis?
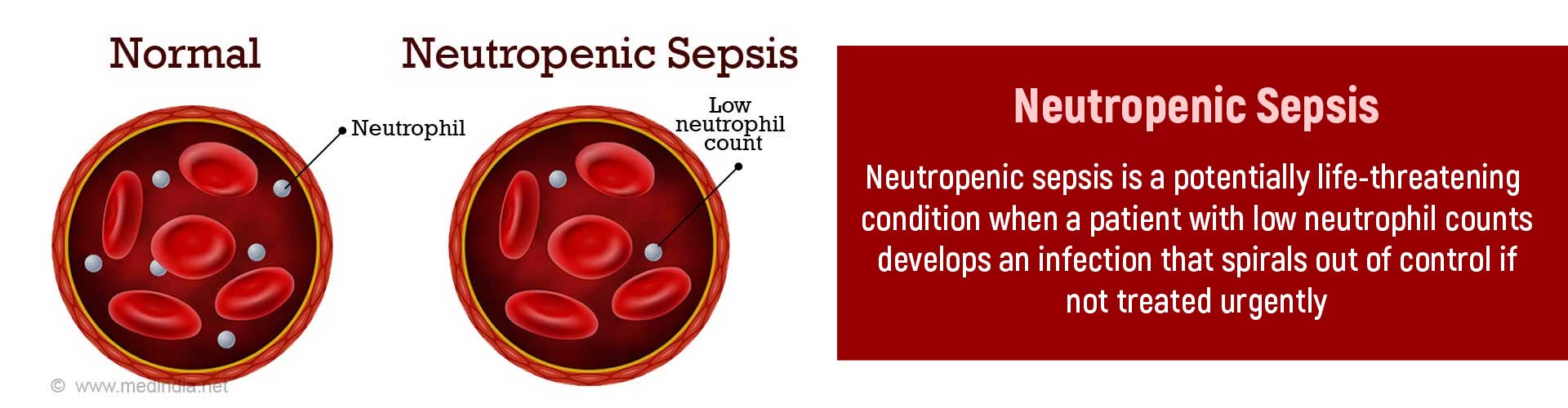
Neutropenic sepsis is the unnatural reduction in neutrophils (an infection-fighting cell) due to an infection, in most cases, a bacterial infection. This condition normally occurs as a complication associated with anticancer treatment and with disorders of the bone marrow. During chemotherapy, the neutrophil count begins to drop within 5 to 7 days. It is at this stage that nearly 70%-100% of individuals are susceptible to bacterial infection that leads to death. The frequency of mortality ranges between 2% and 21%.
What are the Causes of Neutropenic Sepsis?
Neutropenic sepsis occurs due to:
- Chemotherapy - Often observed in patients with solid tumors or in those with hematologic tumors
- Disorders of the bone marrow - Other factors that predispose individuals undergoing chemotherapy to neutropenic sepsis are:
- Prolonged hospital stay - Bacterial infection results from extended hospitalization, use of a catheter, chemotherapy, acute myeloid leukemia
- The type of cancer (eg leukemia and lymphoma affecting the bone marrow)
- Unique features of the affected individual
- Failure of different organs after the initial sepsis is resolved – Circulatory, renal, hepatic