Q: How many forms of CAR T-cell therapy are there?
A: There are 4 kinds of CAR T-cell therapy, which is distinguished by the ability to stimulate cytokine production and by the presence or absence of costimulatory molecules.
Q: What kind of cancers can be treated with CAR T-cell therapy?
A: Currently, CAR T-cell therapy can be used to treat only blood cancers. There is no approved CAR T-cell therapy for solid tumors as yet.
Q: Is CAR T Cell therapy cost-effective?
A: Currently, CAR T-cell therapy is very expensive with Yescarta costing $373,000 and Kymriah costing $475,000. Additional costs are also incurred when treating associated complications and side effects.
Q: How effective is CAR T-cell therapy?
A: In the case of Yescarta, the clinical trial that was conducted with 100 patients showed a remission rate of 51%, which means a little more than half of the patients showed positive effects with CAR T-cell therapy. A recent study published by the American Association of Cancer Research has shown that CAR T-cell therapy in multiple myeloma resulted in nearly 94% of patients showing complete or partial remission.
Q: What is adoptive T cell transfer therapy?
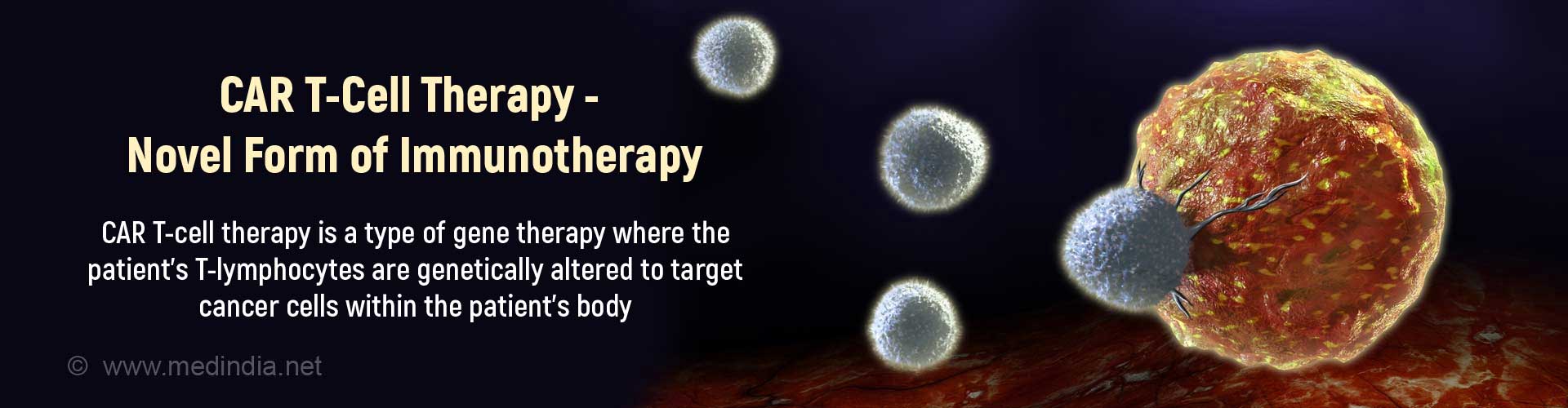
A: Adoptive T cell transfer is a type of personalized immunotherapy where the patient’s own T cells are altered in the laboratory and transplanted back into the body to treat his/her cancer.
Q: What are the limitations of CAR T-cell therapy?
A: CAR T-cells do not recognize internal targets and if they recognize similar antigens on normal cells, the condition of autoimmunity will arise. Another limitation involves antigen loss relapse where the antigen is missing from the tumor cell or is present as a mutated version of the normal on the tumor surface. The changed target is not recognized by CAR.
Q: What is allogenic CAR-T cell therapy?
A: Currently most CAR-T cell treatments involve removing patient’s own T-cells and engineering them into CAR-T cells. This process is called autologous approach and can be time consuming. In allogenic CAR-T cell therapy, the T-cells are obtained from healthy donor and modified and ready to use when needed.