‘The study findings could provide more effective treatment for drug addiction compared with other options such as naltrexone and methadone. It could also shows the potential to deliver other small RNA (microRNA/RNAi) across the blood brain barrier for treatment of CNS diseases.’
Tweet it Now
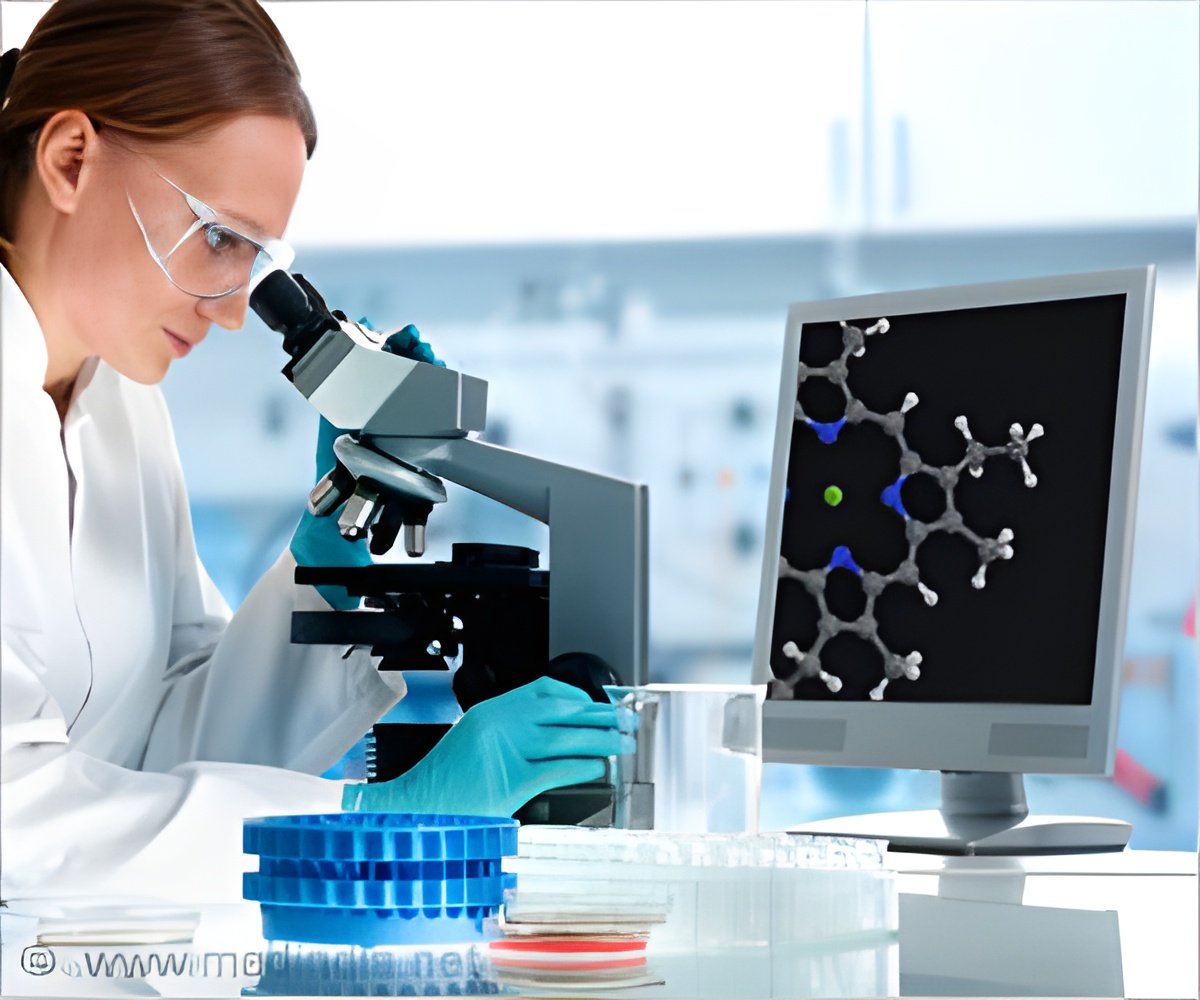
In the present study, in order to deliver siRNA passing through blood-brain barrier (BBB) and then sufficiently getting into brain, Chen-Yu Zhang and colleagues express signal domain of rabies viral glycoprotein (RVG) in exosome membrane. The RVG-exosome-delivered RNAi against opioid receptor mu (MOR) sufficiently down-regulates MOR in mouse brain, and recuses opioid relapse. This research is important for the following reasons:
1) This is the first time to demonstrate that MOR is down-regulated by IV injection of MV-RNAi in vivo. The down-regulation of MOR significantly abolishes morphine relapse. Since MOR-RNAi may serve as a more effective treatment for drug addiction compared with other options such as naltrexone and methadone, it provides a new strategy to control drug addiction.
2) RVG-exosome-delivered RNAi also shows the potential to deliver other small RNA (microRNA/RNAi) to across the blood brain barrier for treatment of more CNS diseases.
Source-Eurekalert