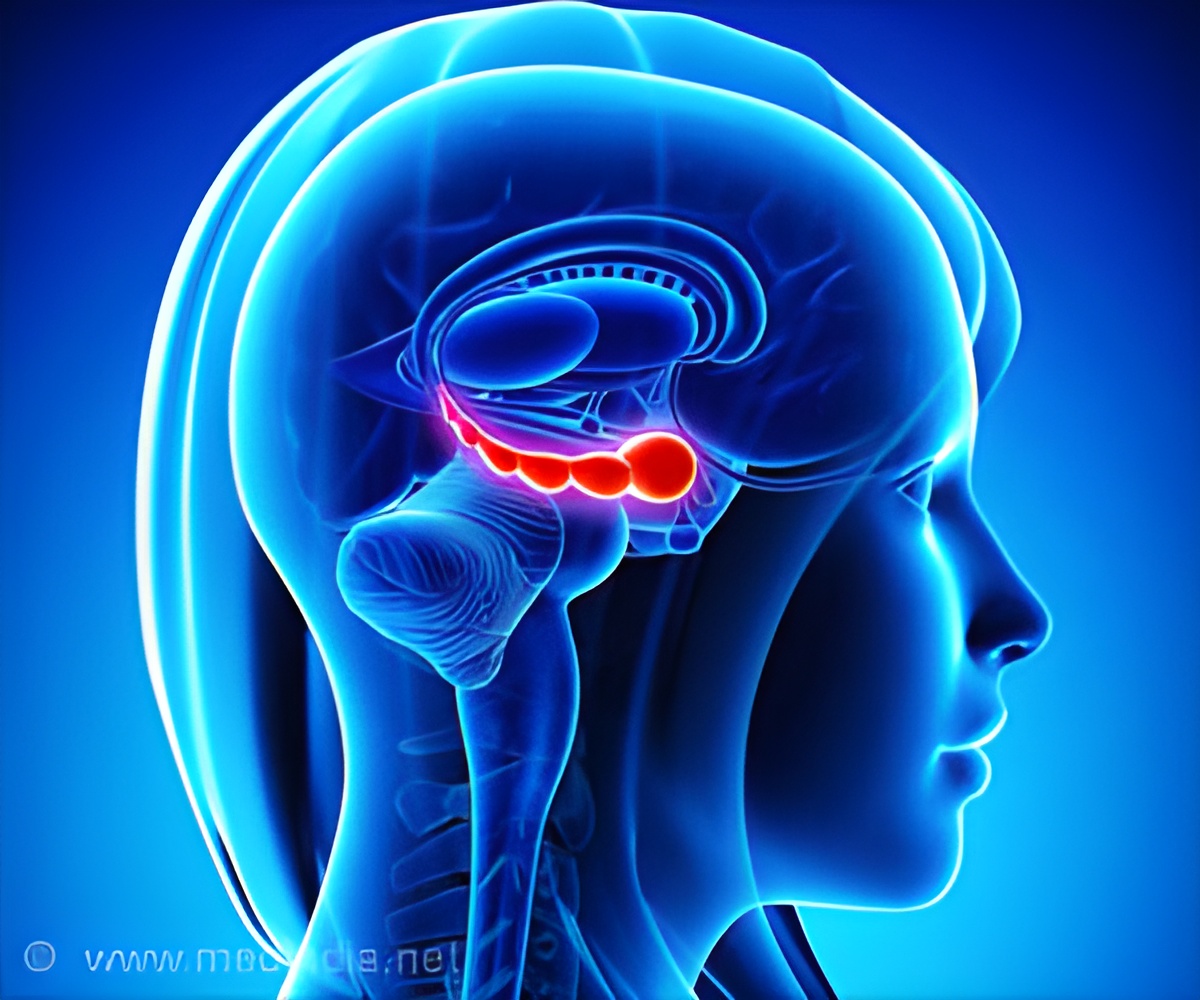
‘Memory flexibility may be rendered by star cells — astrocytes in the brain region called the hippocampus (sea-horse-shaped brain region — vital for memory) by the co-release of brain chemicals called D-serine and glutamate.’
Tweet it Now
It is reported that in brain disorders like autism, schizophrenia, and early stages of Alzheimer's disease, there is a reduction of cognitive flexibility as evidenced by the reduced function of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs — type of brain receptors). The team showed that using astrocyte-specific gene regulation, the release of D-serine could be synthesized through the calcium-activated channel called Best1. This makes astrocytes ideal regulators of NMDAR activity and synaptic plasticity.
"It is hoped that this study will provide valuable insights on how to relieve or treat symptoms of autism, schizophrenia, and early dementia, which are known to reduce cognitive flexibility," says Director C. Justin LEE, who led the study at the Center for Cognition and Sociality, Institute for Basic Science (IB, Daejeon, South Korea.
Source-Medindia












