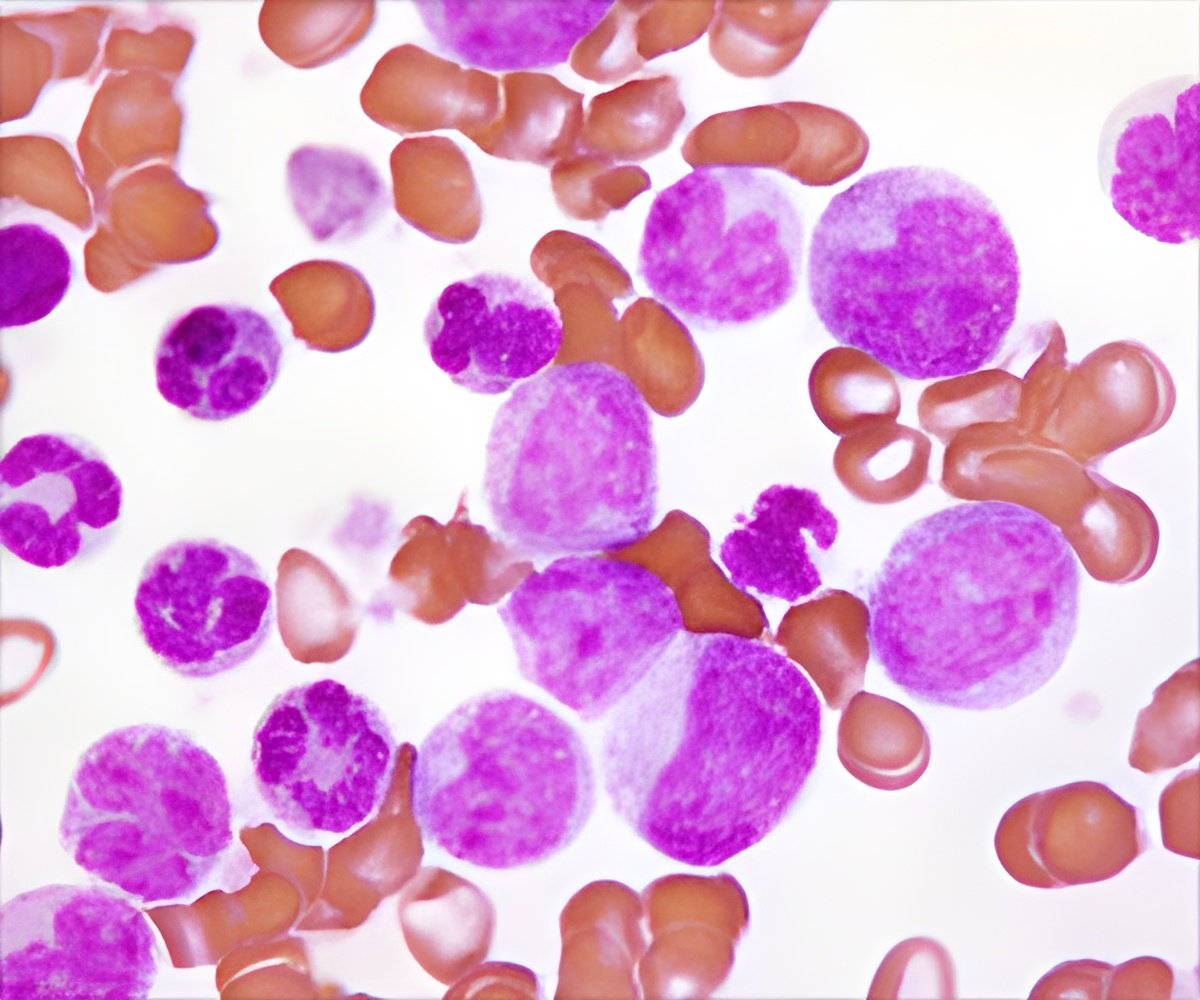
The Fbxw7 protein regulates the production of so-called hematopoietic stem cells, precursors that give rise to all types of blood cells. Without Fbxw7, the body loses the ability to produce blood and eventually succumbs to anemia. Scientists are only beginning to understand why mutated Fbxw7 appears in a significant portion of human tumors, including gastric, prostate, and some breast cancers. The mutation is especially prevalent in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, or T-ALL, a rare but lethal type of pediatric leukemia that causes the over-production of immature white blood cells.
In their experiments, Dr. Aifantis, working in collaboration with graduate student Bryan King and others, began by introducing mutated Fbxw7 into healthy blood stem cells in mice. "We thought the mutation would induce anemia, just as it does when Fbxw7 is deleted," says Dr. Aifantis. But to the researchers' surprise, nothing happened—the stem cells continued to manufacture blood cells.
When the researchers then introduced in mice the mutated Fbxw7 into leukemic blood stem cells—those that overproduce white blood cells and cause leukemia—the cancer accelerated. "We found that the mutation made leukemia stem cells much more aggressive," Dr. Aifantis says.
In follow-up experiments, the researchers showed that Fbxw7 binds to and degrades a protein called Myc, which fuels leukemic stem cells, and has long been associated with many other cancers and the recurrence of cancer after treatment. When Fbxw7 is mutated, Myc is left unchecked, they found, and the population of cancer stem cells swells. This insight also helps explain why healthy blood stem cells seem to "ignore" mutated Fbxw7. Unlike leukemic stem cells, healthy blood stem cells typically lie dormant until the body requires an emergency supply of blood and they rarely express Myc. "Normal blood stem cells express very little Myc because they are not cycling. A mutation does not affect the substrate because the substrate does not exist," says Dr. Aifantis. "Leukemia stem cells, however, do express Myc and Fbxw7 mutations increase its abundance."
The researchers then wondered if eliminating Myc could potentially block leukemia. Indeed, deleting the Myc gene in mice with leukemia depleted leukemic stem cells and stopped the growth of tumors. They achieved the same results in mice and human cell and bone marrow samples of T-ALL using a new class of cancer drug called a BET inhibitor that blocks Myc. "We found that the BET inhibitor could actually kill leukemia stem cells. And without stem cells, the leukemia simply cannot grow," says Dr. Aifantis.
Advertisement
Advertisement