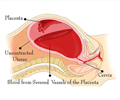
- Post-partum hemorrhage or severe bleeding in mothers after childbirth is the leading cause of maternal death.
- Tranexamic acid is a simple and low-cost drug used in treating post-partum hemorrhage.
- The findings revealed that the drug is capable of reducing bleeding in around 31% of the patients when given within three hours.
The study findings also showed that the drug was capable of reducing the need for surgery to control bleeding by 36%
Postpartum hemorrhage or severe bleeding that occurs in mothers after childbirth is the leading cause of maternal death worldwide. Around 100,000 women may die every year after childbirth. The condition occurs when there is more than 500ml of blood loss within 24 hours after childbirth.
The deaths due to postpartum hemorrhage are mostly either in low-and middle-income countries. Although, giving birth in a healthy facility increases survival in post-partum hemorrhage, there are still women who die from the condition even within the hospitals.
Research Study
The research trial WOMAN (World Maternal Antifibrinolytic) was conducted on mothers from 193 hospitals in 21 countries included mainly Africa and Asia.
There were no side-effects and researchers proved tranexamic acid to be a frontline treatment for post-partum hemorrhage.
Ian Roberts, Professor of Clinical Trials at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who co-led the study, said, "The researchers who invented tranexamic acid more than 50 years ago hoped it would reduce deaths from post-partum hemorrhage, but they couldn't persuade obstetricians at the time to conduct a trial. Now we finally have these results that we hope can help save women's lives around the world."
Tim Knott, Senior Partner in Innovations at Wellcome Trust, said, "Globally, severe bleeding in childbirth remains one of the main causes of maternal death - with alarming numbers of women dying in many low- and middle-income countries. The WOMAN Trial team undertook a hugely important and incredibly ambitious study. Their work stands to make a critical difference in preventing women dying after childbirth."
Even though the trial found the drug to be effective in reducing post-partum hemorrhage, hysterectomy (surgical procedure to remove the uterus) was not prevented. This is because in low-income countries, the procedure is followed immediately after the onset of severe bleeding before tranexamic acid could come to an effect.
Tranexamic Acid
The tranexamic acid belongs to a class of drugs called antifibrinolytics. It was first discovered by a Japanese couple Shosuke and Okamoto.
The drug mainly acts by stopping the blood clots from breaking down. It is available in the form of a tablet to be taken orally.
References
- Haleema Shakur et al. Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage (WOMAN): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet, April 2017 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30638-4
- Tranexamic Acid - (https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a612021.html)
Source-Medindia