Highlights
- Drug-resistant infection is a serious health problem in the world.
- Antibiotic combination therapy can help to overcome deadly drug-resistant bacteria.
- Combining Ceftazidime/avibactam along with aztreonam can help to defeat the drug-resistant infections.
A research team from Cleveland, Ohio has found a new way of combining two different antibiotics together to destroy drug-resistant infections. These antibiotics are capable of destroying the enzyme secreted by bacteria.
When these antibiotics are combined, they may run interference for each other to fight against infections. This will be a new weapon to overcome pernicious infections which are caused by the deadly bacteria that is endemic to hospitals.
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae (CRE) is responsible for about one-third of healthcare-associated infections in the United States. This may also kill nearly half of the victims, according to a study released by Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
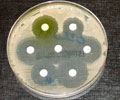
The antibiotic drug combination therapy was found to be effective against 81% of CRE specimens. The studies are conducted under the leadership of Robert A. Bonomo, MD, Professor of Medicine, Pharmacology, Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Microbiology at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and Chief of Medical Service at the Louis Stokes Cleveland Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
Ceftazidime/avibactam antibiotic found to be vulnerable to the neutralizing effect of metallo-beta lactamases.
When these antibiotics are combined, they defeat the drug-resistant infections.
Benefits of Antibiotic Combination Therapy
The new therapy may help doctors to overcome antibiotic neutralizing metallo-beta-lactamases.
Bonomo, explained, "aztreonam skirts around the metallo-beta-lactamase and hits its target--the penicillin-binding proteins."
The bacteria along with aztreonam when attached to the penicillin-binding proteins may build effective cell walls with the drug in a way and could quickly die.
Bonomo, also said, "If we understand the fundamental mechanisms by which bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, we can use what we know to help design better therapies."
The research team also demonstrated the antibiotic therapy to be effective in laboratory models. However, they were soon faced with patients who had no other treatment options.
The treatment was specifically used as a new regimen to treat young kidney transplant patients at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and an elderly woman who received a hip at the University Hospitals.
These patients had various infections which were verged on fatal, yet survived the cutting edge treatment.
The drug is extremely promising for doctors around the world to treat patients with antibiotic-resistant infections. However, the combination approach still needs to go through clinical trials and they must undergo additional research to use as a commonly used treatment.
How to Prevent Drug-resistant Bacteria?
- Infection control procedures must be carefully followed to minimize the spread of bacteria in the hospitals.
- Maintain proper personal hygiene like washing hands properly to minimize the spread of the bacteria in the community.
- Following a careful prescription of antibiotics will minimize the development of more antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria.
- Complete the entire course of antibiotics to avoid infections.
- Michael J. Satlin, Liang Chen, Gopi Patel, Angela Gomez-Simmonds, Gregory Weston, Angela C. Kim, Susan K. Seo, Marnie E. Rosenthal, Steven J. Sperber, Stephen G. Jenkins, Camille L. Hamula, Anne-Catrin Uhlemann, Michael H. Levi, Bettina C. Fries, Yi-Wei Tang, Stefan Juretschko, Albert D. Rojtman, Tao Hong, Barun Mathema, Michael R. Jacobs, Thomas J. Walsh, Robert A. Bonomo, Barry N. Kreiswirth. Bacteremia due to Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE): A Multicenter Clinical and Molecular Epidemiologic Analysis in the Nation's Epicenter for CRE. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2017; DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02349-16
- Antibiotic resistant bacteria - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/antibiotic-resistant-bacteria)
Source-Medindia