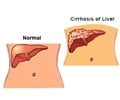
‘Saturated fats may also inhibit the development of alcoholic liver disease by maintaining the growth of intestinal microflora.’
Tweet it Now
In the United States about half of the population drinks alcohol and approximately 38 million people are estimated to engage in binge drinking behavior.This study sought to compare mice bred to preferentially consume high amounts of alcohol (crossed-High Alcohol Preferring, or cHAP, mice) to other mice using a chronic-binge ethanol ingestion model to induce alcoholic liver disease.The mice were randomized and given different diets over a four-week period.
Researchers collected tissue and serum, and discovered that the cHAP mice on a diet of alcohol and water consumed significantly more alcohol than cHAP or other mice maintained on an alcohol diet.
However, cHAP and other mice on the alcohol diet together with the artificial sugar maltodextrin had greater hepatic scarring and overall degree of liver injury compared to mice that consumed a diet of alcohol and water together with maltodextrin.
These data suggest factors other than the total amount of alcohol consumed may affect the degree of alcoholic liver disease development.
Advertisement
This model may provide an additional rodent model to study the effects of ethanol on hepatic pathology that more closely mimics human patterns of ethanol consumption in heavy drinkers.
Advertisement
This position is corroborated by studies demonstrating a protective role for saturated fats in chronic ethanol-fed rodents in which diminished inflammation and decreased micro- and macrovesicular steatosis occurs to promote hepatic fatty oxidation.
Saturated fats may also inhibit the development of alcoholic liver disease by maintaining the growth of intestinal microbiota.
The findings suggest that although cHAP mice consume consistently high/sustained levels of ethanol, other factors such as disparities in specific dietary components, differences in the patterns of alcohol consumption, and timing of feeding relative to peak blood-alcohol content, alter the degree of liver injury in cHAP versus other mice.
"A critical role of the gut microbiome and fecal metabolites is becoming increasingly Appreciated," wrote Irina Kirpich and Craig McClain in an editorial accompanying the study. Marked differences in the composition of the diets used in this study may help explain why mice consuming the highest amounts of alcohol did not develop the most severe liver injury.
Diet and microbiome may be important variables in the different outcomes observed in various experimental alcoholic liver disease models."
Source-Eurekalert