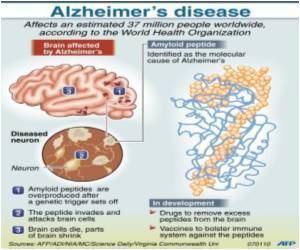
Developed, in part by Dr. Stuart A. Lipton, Director of the Del E. Web Center for Neuroscience, Aging and Stem Cell Research at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), memantine improves symptoms by blocking abnormal activity of glutamate, a chemical that transmits messages between nerve cells.
In the new study, researchers at Sanford-Burnham led by Dr. Lipton unravel exactly how the drug helps Alzheimer's patients without causing serious side effects.
"While memantine is partially effective in treating Alzheimer's disease, one of its major advantages is how safe and well-tolerated it is clinically," said Lipton
Memantine is a particularly safe treatment for Alzheimer's disease because it dampens excessive glutamate signaling that occurs away from synapses without blocking glutamate activity at the synapses.
This is important because interfering with synaptic glutamate signaling would disrupt normal brain activity.
Advertisement
The finding helps explain why the drug is so well tolerated by Alzheimer's patients and might provide hints for the development of future therapies targeting the NMDA receptor and similar cellular machinery in other diseases.
Advertisement
Source-ANI